A(nother) RAF mutation in LCH
- PMID: 24832939
- PMCID: PMC4023415
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-565481
A(nother) RAF mutation in LCH
Abstract
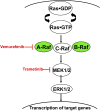
In this issue of Blood, Nelson et al describe a novel somatic ARAF mutation in a child with Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) and demonstrate that the encoded protein has strong gain-of-function properties. Importantly, this mutant A-Raf molecule is sensitive to inhibition by vemurafenib, a potent and selective Raf kinase inhibitor that is Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for the treatment of advanced melanoma. This work thus identifies a new driver mutation in LCH that is potentially actionable in the clinic.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment on
-
Somatic activating ARAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis.Blood. 2014 May 15;123(20):3152-5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-06-511139. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24652991
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

