Long-term treatment of persistent disseminated Nocardia cyriacigeorgica infection
- PMID: 24833199
- PMCID: PMC9428225
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2014.03.007
Long-term treatment of persistent disseminated Nocardia cyriacigeorgica infection
Abstract
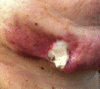
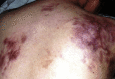
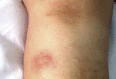
In this paper a disseminated persistent Nocardia cyriacigeorgica infection in an immunocompetent patient is described. The patient's long-term treatment, as well as its implications for managing similar cases in the future, is emphasized. Presenting with high fever, multiple nodules, and ulcerative cutaneous lesions of body sites, the patient was treated with various antimicrobials. Under combined therapy, empyema and arthritis, leading to disseminated nocardiosis, were seen. The overall treatment course was 28 months. It can be concluded that the choice of the antibiotics and optimal duration of treatment are uncertain; therefore the treatment of nocardiosis requires expertise.
Keywords: Chronic infection; Nocardia cyriacigeorgica; Treatment.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primary cutaneous nocardiosis due to Nocardia brasiliensis in an immunocompetent patient.J Dermatol. 2005 Mar;32(3):230-2. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2005.tb00754.x. J Dermatol. 2005. PMID: 15863876 No abstract available.
-
Lymphocutaneous nocardiosis caused by Nocardia brasiliensis in an immunocompetent elderly woman.Int J Dermatol. 2016 Jan;55(1):e45-7. doi: 10.1111/ijd.12988. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Int J Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 26475056 No abstract available.
-
Ulcerative Plaques and Nodules on the Lower Extremity: A Quiz.Acta Derm Venereol. 2017 Jul 6;97(7):866-867. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2659. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017. PMID: 28350040 No abstract available.
-
A rare case of primary cutaneous Nocardia vinacea in an immunocompetent patient: A case report and a review of the literature.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024 Jul;109(3):116307. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2024.116307. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38733753 Review.
-
Disseminated nocardiosis caused by Nocardia elegans: a case report and review of the literature.Infection. 2018 Oct;46(5):705-710. doi: 10.1007/s15010-018-1144-2. Epub 2018 May 8. Infection. 2018. PMID: 29737456 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolated Nocardiosis, an Unrecognized Primary Immunodeficiency?Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 20;11:590239. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.590239. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33193422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Nocardia Infections: A Review of Pulmonary Nocardiosis.Cureus. 2015 Aug 15;7(8):e304. doi: 10.7759/cureus.304. Cureus. 2015. PMID: 26430578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nocardia Arthritis: 3 Cases and Literature Review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Oct;94(42):e1671. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001671. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26496274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Occupational hazard in an immunosuppressed patient.Frontline Gastroenterol. 2019 Jul 23;12(1):74-76. doi: 10.1136/flgastro-2019-101221. eCollection 2021. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 33489071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sorrell T.C., Mitchell D.H., Iredell J.R., Chen S.C.-A. In: Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. 7th ed. Mandell G.L., Bennett J.E., Dolin R., editors. Elsevier Churchill Livingston; Philadelphia: 2010. Nocardia species; pp. 3199–3207.
-
- Ozan F., Koyuncu Ş., Kızılay C., Özgenç O. The nocardia farcinica infection developing after total knee arthroplasty surgery. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2013;47:212–217. - PubMed
-
- Lewis K.E., Ebden P., Wooster S.L., Rees J., Harrison G.A.J. Multi-system infection with Nocardia farcinia – therapy with linezolid and minocycline. J Infect. 2003;46:199–202. - PubMed
-
- Boiron P., Provost F. In-vitro susceptibility testing of Nocardia spp. and its taxonomic implication. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988;22:623–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical