DNA damage response in plants: conserved and variable response compared to animals
- PMID: 24833228
- PMCID: PMC4009792
- DOI: 10.3390/biology2041338
DNA damage response in plants: conserved and variable response compared to animals
Abstract
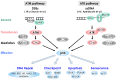
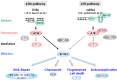
The genome of an organism is under constant attack from endogenous and exogenous DNA damaging factors, such as reactive radicals, radiation, and genotoxins. Therefore, DNA damage response systems to sense DNA damage, arrest cell cycle, repair DNA lesions, and/or induce programmed cell death are crucial for maintenance of genomic integrity and survival of the organism. Genome sequences revealed that, although plants possess many of the DNA damage response factors that are present in the animal systems, they are missing some of the important regulators, such as the p53 tumor suppressor. These observations suggest differences in the DNA damage response mechanisms between plants and animals. In this review the DNA damage responses in plants and animals are compared and contrasted. In addition, the function of SUPPRESSOR OF GAMMA RESPONSE 1 (SOG1), a plant-specific transcription factor that governs the robust response to DNA damage, is discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SOG1: a master regulator of the DNA damage response in plants.Genes Genet Syst. 2016;90(4):209-16. doi: 10.1266/ggs.15-00011. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Genes Genet Syst. 2016. PMID: 26617076 Review.
-
An insight into the mechanism of DNA damage response in plants- role of SUPPRESSOR OF GAMMA RESPONSE 1: An overview.Mutat Res. 2020 Jan-Apr;819-820:111689. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2020.111689. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 32004947 Review.
-
The role of SOG1, a plant-specific transcriptional regulator, in the DNA damage response.Plant Signal Behav. 2014;9(4):e28889. doi: 10.4161/psb.28889. Plant Signal Behav. 2014. PMID: 24736489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying the target genes of SUPPRESSOR OF GAMMA RESPONSE 1, a master transcription factor controlling DNA damage response in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2018 May;94(3):439-453. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13866. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Plant J. 2018. PMID: 29430765
-
ATM-mediated phosphorylation of SOG1 is essential for the DNA damage response in Arabidopsis.EMBO Rep. 2013 Sep;14(9):817-22. doi: 10.1038/embor.2013.112. Epub 2013 Aug 2. EMBO Rep. 2013. PMID: 23907539 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Arabidopsis thaliana DNA Damage Response Mutants Challenged with Genotoxic Agents-A Different Experimental Approach to Investigate the TDP1α and TDP1β Genes.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jan 19;16(1):103. doi: 10.3390/genes16010103. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858650 Free PMC article.
-
Modulatory Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Root Development in Model Plant of Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Sep 16;11:485932. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.485932. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33042167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: MicroRNA Signatures in Plant Genome Stability and Genotoxic Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Apr 22;12:683302. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.683302. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33968124 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response of the Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii to the DNA Damaging Agent Zeocin.Cells. 2019 Jul 17;8(7):735. doi: 10.3390/cells8070735. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31319624 Free PMC article.
-
It Is Just a Matter of Time: Balancing Homologous Recombination and Non-homologous End Joining at the rDNA Locus During Meiosis.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 28;12:773052. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.773052. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34777453 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beck C.B. An Introduction to Plant Structure and Development. 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2010.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

