α5β1 integrin signaling mediates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced inflammation and early atherosclerosis
- PMID: 24833794
- PMCID: PMC4096780
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303863
α5β1 integrin signaling mediates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced inflammation and early atherosclerosis
Abstract
Objective: Endothelial cell activation drives early atherosclerotic plaque formation. Both fibronectin deposition and accumulation of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) occur early during atherogenesis, and both are implicated in enhanced endothelial cell activation. However, interplay between these responses has not been established. The objective of our study was to determine whether endothelial matrix composition modulates the inflammatory properties of oxLDL.
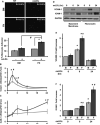
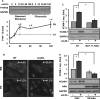
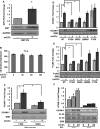
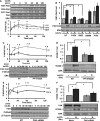
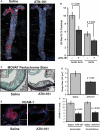
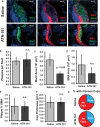
Approach and results: We now show that oxLDL-induced nuclear factor-κB activation, proinflammatory gene expression, and monocyte binding are significantly enhanced when endothelial cells are attached to fibronectin compared with basement membrane proteins. This enhanced response does not result from altered oxLDL receptor expression, oxLDL uptake, or reactive oxygen species production, but results from oxLDL-induced activation of the fibronectin-binding integrin α5β1. Preventing α5β1 signaling (blocking antibodies, knockout cells) inhibits oxLDL-induced nuclear factor-κB activation and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression. Furthermore, oxLDL drives α5β1-dependent integrin signaling through the focal adhesion kinase pathway, and focal adhesion kinase inhibition (PF-573228, small interfering RNA) blunts oxLDL-induced nuclear factor-κB activation, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression, and monocyte adhesion. Last, treatment with the α5β1 signaling inhibitor, ATN-161, significantly blunts atherosclerotic plaque development in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice, characterized by reduced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and macrophage accumulation without affecting fibrous cap size.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that α5β1-mediated cross-talk between fibronectin and oxLDL regulates inflammation in early atherogenesis and that therapeutics that inhibit α5 integrins may reduce inflammation without adversely affecting plaque structure.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; fibronectins; inflammation; integrin alpha5beta1; lipoproteins, LDL.
© 2014 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial FN (Fibronectin) Deposition by α5β1 Integrins Drives Atherogenic Inflammation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Nov;38(11):2601-2614. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311705. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 30354234 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized LDL induces FAK-dependent RSK signaling to drive NF-κB activation and VCAM-1 expression.J Cell Sci. 2016 Apr 15;129(8):1580-91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.182097. Epub 2016 Feb 18. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 26906414 Free PMC article.
-
RGC-32 (Response Gene to Complement 32) Deficiency Protects Endothelial Cells From Inflammation and Attenuates Atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Apr;38(4):e36-e47. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.310656. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29449334 Free PMC article.
-
Postprandial lipoproteins and the molecular regulation of vascular homeostasis.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):446-64. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23774609 Review.
-
The Initial Human Atherosclerotic Lesion and Lipoprotein Modification-A Deep Connection.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 25;22(21):11488. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111488. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768918 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms and Consequences of Defective Efferocytosis in Atherosclerosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Jan 8;4:86. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00086. eCollection 2017. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 29379788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin signaling in atherosclerosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Jun;74(12):2263-2282. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2490-4. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28246700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EphA2 signaling within integrin adhesions regulates fibrillar adhesion elongation and fibronectin deposition.Matrix Biol. 2021 Sep;103-104:1-21. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2021.09.001. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Matrix Biol. 2021. PMID: 34537369 Free PMC article.
-
CD40L and Its Receptors in Atherothrombosis-An Update.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017 Jun 20;4:40. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00040. eCollection 2017. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017. PMID: 28676852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Type 1 Diabetes-Resistance Locus Idd22 Controls Trafficking of Autoreactive CTLs into the Pancreatic Islets of NOD Mice.J Immunol. 2017 Dec 15;199(12):3991-4000. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1602037. Epub 2017 Nov 6. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29109122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim JA, Territo MC, Wayner E, Carlos TM, Parhami F, Smith CW, Haberland ME, Fogelman AM, Berliner JA. Partial characterization of leukocyte binding molecules on endothelial cells induced by minimally oxidized LDL. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994;14:427–433. - PubMed
-
- Amberger A, Maczek C, Jurgens G, Michaelis D, Schett G, Trieb K, Eberl T, Jindal S, Xu Q, Wick G. Co-expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, ELAM-1 and Hsp60 in human arterial and venous endothelial cells in response to cytokines and oxidized low-density lipoproteins. Cell Stress Chaperones. 1997;2:94–103. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mehta J, Sanada N, Hu C, Chen J, Dandapat A, Sugawara F, Satoh H, Inoue K, Kawase Y, Jishage K-i, Suzuki H, Takeya M, Schnackenberg L, Beger R, Hermonat P, Thomas M, Sawamura T. Deletion of LOX-1 reduces atherogenesis in LDLR knockout mice fed high cholesterol diet. Circulation research. 2007;100:1634–1642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

