Formulation and delivery of itraconazole to the brain using a nanolipid carrier system
- PMID: 24833900
- PMCID: PMC4014385
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S57565
Formulation and delivery of itraconazole to the brain using a nanolipid carrier system
Abstract
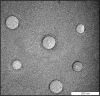
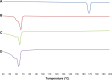
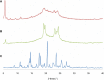
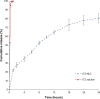
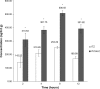
The objectives of this study were to develop and characterize itraconazole (ITZ)-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) and to study their potential for drug delivery into the brain. Precirol(®) ATO 5 and Transcutol(®) HP were selected as the lipid phase, and Tween(®) 80 and Solutol(®) HS15 as surfactants. The ITZ-NLCs were prepared by a hot and high-pressure homogenization method. The entrapment efficiency for the best formulation batch was analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography and was found to be 70.5%±0.6%. The average size, zeta potential, and polydispersity index for the ITZ-NLCs used for animal studies were found to be 313.7±15.3 nm, -18.7±0.30 mV, and 0.562±0.070, respectively. Transmission electron microscopy confirmed that ITZ-NLCs were spherical in shape, with a size of less than 200 nm. Differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffractometry analysis showed that ITZ was encapsulated in the lipid matrix and present in the amorphous form. The in vitro release study showed that ITZ-NLCs achieved a sustained release, with cumulative release of 80.6%±5.3% up to 24 hours. An in vivo study showed that ITZ-NLCs could increase the ITZ concentration in the brain by almost twofold. These results suggest that ITZ-NLCs can be exploited as nanocarriers to achieve sustained release and brain-targeted delivery.
Keywords: brain delivery; lipid nanoparticles; nanostructured lipid carrier.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased dissolution and oral absorption of itraconazole/Soluplus extrudate compared with itraconazole nanosuspension.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013 Nov;85(3 Pt B):1285-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013. PMID: 23562534
-
Development of PLGA-based itraconazole injectable nanospheres for sustained release.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:4521-31. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S54040. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 24311942 Free PMC article.
-
Itraconazole Loaded Micelle Based on Methoxy Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Poly(D, L-Lactic Acid) for Ocular Drug Delivery: In vitro and in vivo Evaluation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 May 22;20:6447-6462. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S521127. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40420914 Free PMC article.
-
Borneol and poly (ethylene glycol) dual modified BSA nanoparticles as an itraconazole vehicle for brain targeting.Int J Pharm. 2020 Feb 15;575:119002. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.119002. Epub 2019 Dec 29. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31893546
-
Targeted brain delivery of itraconazole via RVG29 anchored nanoparticles.J Drug Target. 2011 Apr;19(3):228-34. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2010.492523. Epub 2010 Jun 14. J Drug Target. 2011. PMID: 20540685
Cited by
-
Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers for Bioactive Delivery.Front Chem. 2021 Apr 23;9:580118. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.580118. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 33981670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and evaluation of nanostructured lipid carrier-based hydrogel for topical delivery of 5-fluorouracil.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Oct 5;11:5067-5077. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S117511. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27785014 Free PMC article.
-
Itraconazole loaded nano-structured lipid carrier for topical ocular delivery: Optimization and evaluation.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan;29(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.11.006. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002390 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal diseases: could nanostructured drug delivery systems be a novel paradigm for therapy?Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Aug 8;11:3715-30. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S93105. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27540288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Case of Histoplasmosis with Central Nervous System Relapse after Itraconazole Therapy Needs Further Research.Cureus. 2020 Feb 21;12(2):e7064. doi: 10.7759/cureus.7064. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32226666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wissing SA, Kayser O, Müller RH. Solid lipid nanoparticles for parenteral drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56(9):1257–1272. - PubMed
-
- Müller RH, Mäder K, Gohla S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery – a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;50(1):161–177. - PubMed
-
- Mehnert W, Mäder K. Solid lipid nanoparticles: production, characterization and applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47(2–3):165–196. - PubMed
-
- Müller RH, Radtke M, Wissing SA. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic and dermatological preparations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002;54(Suppl 1):S131–S155. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

