The orexinergic system influences conditioned odor aversion learning in the rat: a theory on the processes and hypothesis on the circuit involved
- PMID: 24834041
- PMCID: PMC4018543
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00164
The orexinergic system influences conditioned odor aversion learning in the rat: a theory on the processes and hypothesis on the circuit involved
Abstract
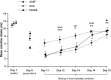
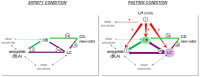
A large variety of behaviors that are essential for animal survival depend on the perception and processing of surrounding smells present in the natural environment. In particular, food-search behavior, which is conditioned by hunger, is directly driven by the perception of odors associated with food, and feeding status modulates olfactory sensitivity. The orexinergic hypothalamic peptide orexin A (OXA), one of the central and peripheral hormones that triggers food intake, has been shown to increase olfactory sensitivity in various experimental conditions including the conditioned odor aversion learning paradigm (COA). COA is an associative task that corresponds to the association between an olfactory conditioned stimulus (CS) and a delayed gastric malaise. Previous studies have shown that this association is formed only if the delay separating the CS presentation from the malaise is short, suggesting that the memory trace of the odor is relatively unstable. To test the selectivity of the OXA system in olfactory sensitivity, a recent study compared the effects of fasting and of central infusion of OXA during the acquisition of COA. Results showed that the increased olfactory sensitivity induced by fasting and by OXA infusion was accompanied by enhanced COA learning performances. In reference to the duration of action of OXA, the present work details the results obtained during the successive COA extinction tests and suggests a hypothesis concerning the role of the OXA component of fasting on the memory processes underlying CS-malaise association during COA. Moreover, referring to previous data in the literature we suggest a functional circuit model where fasting modulates olfactory memory processes through direct and/or indirect activation of particular OXA brain targets including the olfactory bulb, the locus coeruleus (LC) and the amygdala.
Keywords: associative learning; fasting; olfactory memory; orexin; rat.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

