Remission of disseminated cancer after systemic oncolytic virotherapy
- PMID: 24835528
- PMCID: PMC4225126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.04.003
Remission of disseminated cancer after systemic oncolytic virotherapy
Abstract
MV-NIS is an engineered measles virus that is selectively destructive to myeloma plasma cells and can be monitored by noninvasive radioiodine imaging of NIS gene expression. Two measles-seronegative patients with relapsing drug-refractory myeloma and multiple glucose-avid plasmacytomas were treated by intravenous infusion of 10(11) TCID50 (50% tissue culture infectious dose) infectious units of MV-NIS. Both patients responded to therapy with M protein reduction and resolution of bone marrow plasmacytosis. Further, one patient experienced durable complete remission at all disease sites. Tumor targeting was clearly documented by NIS-mediated radioiodine uptake in virus-infected plasmacytomas. Toxicities resolved within the first week after therapy. Oncolytic viruses offer a promising new modality for the targeted infection and destruction of disseminated cancer.
Copyright © 2014 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
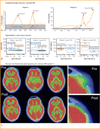

Comment in
-
Taming measles virus to create an effective cancer therapeutic.Mayo Clin Proc. 2014 Jul;89(7):863-5. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.04.009. Epub 2014 May 14. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014. PMID: 24835529 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tong AW, Senzer N, Cerullo V, Templeton NS, Hemminki A, Nemunaitis J. Oncolytic viruses for induction of anti-tumor immunity. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13(9):1750–1760. - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV. An overview of the progress in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Exp Rev Hematol. 2014;7(1):5–7. - PubMed
-
- Dingli D, Peng KW, Harvey ME, et al. Image-guided radiovirotherapy for multiple myeloma using a recombinant measles virus expressing the thyroidal sodium iodide symporter. Blood. 2004;103(5):1641–1646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

