The association between within-visit blood pressure variability and carotid artery atherosclerosis in general population
- PMID: 24835667
- PMCID: PMC4024014
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097760
The association between within-visit blood pressure variability and carotid artery atherosclerosis in general population
Abstract
Objectives: To determine whether within-visit blood pressure (BP) variability based on three measurements over minutes is associated with increased carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) and plaque in a general population.
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was performed in 2007, and a total of 1222 Beijing community residents aged 50-79 years belonging to part of the Chinese Multi-Provincial Cohort Study (CMCS) were recruited in this study. BP was measured three times at 5-minute intervals during a single visit, and the maximum absolute difference (MAD) between any two readings of three measurements was used to indicate within-visit BP variability. Carotid IMT and plaque scanned by B-mode ultrasound were identified as the surrogate end points in the intermediate stage of atherosclerosis.
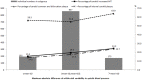
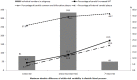
Results: After adjustment for established cardiovascular risk factors, the odds ratio (OR) (95% confidence interval (CI)) for increased carotid IMT and internal carotid plaque associated with the highest within-visit diastolic BP (DBP) variability (MAD > mean + standard deviation (SD)) compared with participants in the lowest within-visit DBP variability (MAD ≤ mean -SD) was 4.92 (1.48-16.42) and 6.07 (1.31-28.10), respectively, in the normotensives (P = 0.01; P = 0.02). The OR (95% CI) for internal carotid plaque associated with the highest within-visit systolic BP (SBP) variability (MAD >mean +SD) compared with participants in the lowest within-visit SBP variability (MAD ≤ mean -SD) was 3.54 (1.26-10.00) in the hypertensives on antihypertensive therapy (P = 0.02).
Conclusions: Within-visit DBP variability was associated with increased carotid IMT and internal carotid plaque in the normotensive population, and within-visit SBP variability was associated with internal carotid plaque in hypertensive patients undergoing antihypertensive therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A (2008) Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet 371: 1513–1518. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, et al. (2003) Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 42: 1206–1252. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, et al. (2007) 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 25: 1105–1187. - PubMed
-
- Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, Falkner BE, Graves J, et al. (2005) Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation 111: 697–716. - PubMed
-
- Rothwell PM, Howard SC, Dolan E, O'Brien E, Dobson JE, et al. (2010) Effects of beta blockers and calcium-channel blockers on within-individual variability in blood pressure and risk of stroke. Lancet Neurol 9: 469–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

