TET1-mediated hydroxymethylation facilitates hypoxic gene induction in neuroblastoma
- PMID: 24835990
- PMCID: PMC4516227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.040
TET1-mediated hydroxymethylation facilitates hypoxic gene induction in neuroblastoma
Abstract
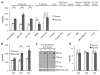
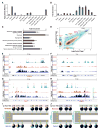
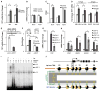
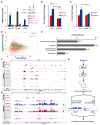
The ten-eleven-translocation 5-methylcytosine dioxygenase (TET) family of enzymes catalyzes the conversion of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC), a modified cytosine base that facilitates gene expression. Cells respond to hypoxia by inducing a transcriptional program regulated in part by oxygen-dependent dioxygenases that require Fe(II) and α-ketoglutarate. Given that the TET enzymes also require these cofactors, we hypothesized that the TETs regulate the hypoxia-induced transcriptional program. Here, we demonstrate that hypoxia increases global 5-hmC levels, with accumulation of 5-hmC density at canonical hypoxia response genes. A subset of 5-hmC gains colocalize with hypoxia response elements facilitating DNA demethylation and HIF binding. Hypoxia results in transcriptional activation of TET1, and full induction of hypoxia-responsive genes and global 5-hmC increases require TET1. Finally, we show that 5-hmC increases and TET1 upregulation in hypoxia are HIF-1 dependent. These findings establish TET1-mediated 5-hmC changes as an important epigenetic component of the hypoxic response.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Branco MR, Ficz G, Reik W. Uncovering the role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the epigenome. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:7–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

