β-Catenin-regulated myeloid cell adhesion and migration determine wound healing
- PMID: 24837430
- PMCID: PMC4089463
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI62059
β-Catenin-regulated myeloid cell adhesion and migration determine wound healing
Abstract
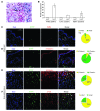
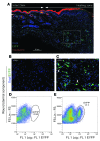
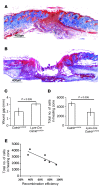
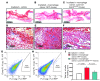
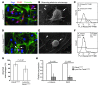
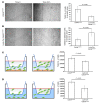
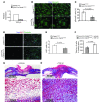
A β-catenin/T cell factor-dependent transcriptional program is critical during cutaneous wound repair for the regulation of scar size; however, the relative contribution of β-catenin activity and function in specific cell types in the granulation tissue during the healing process is unknown. Here, cell lineage tracing revealed that cells in which β-catenin is transcriptionally active express a gene profile that is characteristic of the myeloid lineage. Mice harboring a macrophage-specific deletion of the gene encoding β-catenin exhibited insufficient skin wound healing due to macrophage-specific defects in migration, adhesion to fibroblasts, and ability to produce TGF-β1. In irradiated mice, only macrophages expressing β-catenin were able to rescue wound-healing deficiency. Evaluation of scar tissue collected from patients with hypertrophic and normal scars revealed a correlation between the number of macrophages within the wound, β-catenin levels, and cellularity. Our data indicate that β-catenin regulates myeloid cell motility and adhesion and that β-catenin-mediated macrophage motility contributes to the number of mesenchymal cells and ultimate scar size following cutaneous injury.
Figures
References
-
- Gottrup F. A specialized wound-healing center concept: importance of a multidisciplinary department structure and surgical treatment facilities in the treatment of chronic wounds. Am J Surg. 2004;187(5A):38S–43S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

