Synthetic triterpenoid induces 15-PGDH expression and suppresses inflammation-driven colon carcinogenesis
- PMID: 24837432
- PMCID: PMC4089461
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI69672
Synthetic triterpenoid induces 15-PGDH expression and suppresses inflammation-driven colon carcinogenesis
Abstract
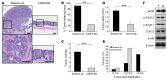
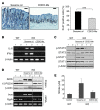
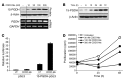
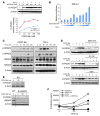
Colitis-associated colon cancer (CAC) develops as a result of inflammation-induced epithelial transformation, which occurs in response to inflammatory cytokine-dependent downregulation of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) and subsequent suppression of prostaglandin metabolism. Agents that both enhance 15-PGDH expression and suppress cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) production may more effectively prevent CAC. Synthetic triterpenoids are a class of small molecules that suppress COX-2 as well as inflammatory cytokine signaling. Here, we found that administration of the synthetic triterpenoid 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-C28-methyl ester (CDDO-Me) suppresses CAC in mice. In a spontaneous, inflammation-driven intestinal neoplasia model, deletion of Smad4 specifically in T cells led to progressive production of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IFN-γ, iNOS, IL-6, IL-1β; as well as activation of STAT1 and STAT3; along with suppression of 15-PGDH expression. Oral administration of CDDO-Me to mice with SMAD4-deficient T cells increased survival and suppressed intestinal epithelial neoplasia by decreasing production of inflammatory mediators and increasing expression of 15-PGDH. Induction of 15-PGDH by CDDO-Me was dose dependent in epithelial cells and was abrogated following treatment with TGF-β signaling inhibitors in vitro. Furthermore, CDDO-Me-dependent 15-PGDH induction was not observed in Smad3-/- mice. Similarly, CDDO-Me suppressed azoxymethane plus dextran sodium sulfate-induced carcinogenesis in wild-type animals, highlighting the potential of small molecules of the triterpenoid family as effective agents for the chemoprevention of CAC in humans.
Figures



Comment in
-
Colorectal cancer: chemopreventive action of synthetic triterpenoids in CRC.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Jul;11(7):395. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.87. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24890280 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Smad4-deficient T cells promote colitis-associated colon cancer via an IFN-γ-dependent suppression of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 15;13:932412. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.932412. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36045676 Free PMC article.
-
Concerted actions of ameliorated colitis, aberrant crypt foci inhibition and 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase induction by sonic hedgehog inhibitor led to prevention of colitis-associated cancer.Int J Cancer. 2016 Mar 15;138(6):1482-93. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29892. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26476372
-
Sonic hedgehog inhibitors prevent colitis-associated cancer via orchestrated mechanisms of IL-6/gp130 inhibition, 15-PGDH induction, Bcl-2 abrogation, and tumorsphere inhibition.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 16;7(7):7667-82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6765. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26716648 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011 Nov;96(1-4):37-40. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2011.06.005. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011. PMID: 21763448 Review.
-
15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) and lung cancer.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007 May;83(3):203-8. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2007.01.007. Epub 2007 Jan 17. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007. PMID: 17481556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of natural products in revealing NRF2 function.Nat Prod Rep. 2020 Jun 1;37(6):797-826. doi: 10.1039/c9np00061e. Epub 2020 May 13. Nat Prod Rep. 2020. PMID: 32400766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Vitamin D in Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 13;19(9):2736. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092736. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30216977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bardoxolone Methyl Prevents Mesenteric Fat Deposition and Inflammation in High-Fat Diet Mice.ScientificWorldJournal. 2015;2015:549352. doi: 10.1155/2015/549352. Epub 2015 Nov 5. ScientificWorldJournal. 2015. PMID: 26618193 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory natural product goniothalamin reduces colitis-associated and sporadic colorectal tumorigenesis.Carcinogenesis. 2017 Jan;38(1):51-63. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgw112. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Carcinogenesis. 2017. PMID: 27797827 Free PMC article.
-
Smad4-deficient T cells promote colitis-associated colon cancer via an IFN-γ-dependent suppression of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 15;13:932412. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.932412. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36045676 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

