A unified test of linkage analysis and rare-variant association for analysis of pedigree sequence data
- PMID: 24837662
- PMCID: PMC4157619
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.2895
A unified test of linkage analysis and rare-variant association for analysis of pedigree sequence data
Abstract
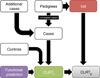
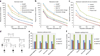
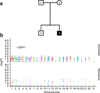
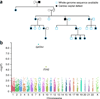
High-throughput sequencing of related individuals has become an important tool for studying human disease. However, owing to technical complexity and lack of available tools, most pedigree-based sequencing studies rely on an ad hoc combination of suboptimal analyses. Here we present pedigree-VAAST (pVAAST), a disease-gene identification tool designed for high-throughput sequence data in pedigrees. pVAAST uses a sequence-based model to perform variant and gene-based linkage analysis. Linkage information is then combined with functional prediction and rare variant case-control association information in a unified statistical framework. pVAAST outperformed linkage and rare-variant association tests in simulations and identified disease-causing genes from whole-genome sequence data in three human pedigrees with dominant, recessive and de novo inheritance patterns. The approach is robust to incomplete penetrance and locus heterogeneity and is applicable to a wide variety of genetic traits. pVAAST maintains high power across studies of monogenic, high-penetrance phenotypes in a single pedigree to highly polygenic, common phenotypes involving hundreds of pedigrees.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HL098179/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH099134/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100406/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091374/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HG005846/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM104390/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059290/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00HG005846/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HL098179/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA164138/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM59290/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R44 HG006579/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094400/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R44HG006579/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109758/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

