The effects of gut microbiota on CNS function in humans
- PMID: 24838095
- PMCID: PMC4153780
- DOI: 10.4161/gmic.29232
The effects of gut microbiota on CNS function in humans
Abstract
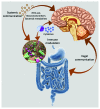
The role of the gastrointestinal microbiota in human brain development and function is an area of increasing interest and research. Preclinical models suggest a role for the microbiota in broad aspects of human health, including mood, cognition, and chronic pain. Early human studies suggest that altering the microbiota with beneficial bacteria, or probiotics, can lead to changes in brain function, as well as subjective reports of mood. As the mechanisms of bidirectional communication between the brain and microbiota are better understood, it is expected that these pathways will be harnessed to provide novel methods to enhance health and treat disease.
Keywords: anxiety; brain-gut axis; depression; microbiota; probiotic.
Figures
References
-
- Azad MB, Konya T, Maughan H, Guttman DS, Field CJ, Chari RS, Sears MR, Becker AB, Scott JA, Kozyrskyj AL, CHILD Study Investigators Gut microbiota of healthy Canadian infants: profiles by mode of delivery and infant diet at 4 months. CMAJ. 2013;185:385–94. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.121189. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials