Alkemio: association of chemicals with biomedical topics by text and data mining
- PMID: 24838570
- PMCID: PMC4086102
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku432
Alkemio: association of chemicals with biomedical topics by text and data mining
Abstract
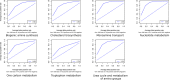
The PubMed® database of biomedical citations allows the retrieval of scientific articles studying the function of chemicals in biology and medicine. Mining millions of available citations to search reported associations between chemicals and topics of interest would require substantial human time. We have implemented the Alkemio text mining web tool and SOAP web service to help in this task. The tool uses biomedical articles discussing chemicals (including drugs), predicts their relatedness to the query topic with a naïve Bayesian classifier and ranks all chemicals by P-values computed from random simulations. Benchmarks on seven human pathways showed good retrieval performance (areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves ranged from 73.6 to 94.5%). Comparison with existing tools to retrieve chemicals associated to eight diseases showed the higher precision and recall of Alkemio when considering the top 10 candidate chemicals. Alkemio is a high performing web tool ranking chemicals for any biomedical topics and it is free to non-commercial users.
Availability: http://cbdm.mdc-berlin.de/∼medlineranker/cms/alkemio.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MedlineRanker: flexible ranking of biomedical literature.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jul;37(Web Server issue):W141-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp353. Epub 2009 May 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19429696 Free PMC article.
-
Using cited references to improve the retrieval of related biomedical documents.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Mar 27;14:113. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-113. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23537461 Free PMC article.
-
BioReader: a text mining tool for performing classification of biomedical literature.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Feb 4;19(Suppl 13):57. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2607-x. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30717659 Free PMC article.
-
PubMed and beyond: a survey of web tools for searching biomedical literature.Database (Oxford). 2011 Jan 18;2011:baq036. doi: 10.1093/database/baq036. Print 2011. Database (Oxford). 2011. PMID: 21245076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accessing biomedical literature in the current information landscape.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1159:11-31. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0709-0_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24788259 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Using systems medicine to identify a therapeutic agent with potential for repurposing in inflammatory bowel disease.Dis Model Mech. 2020 Nov 27;13(11):dmm044040. doi: 10.1242/dmm.044040. Dis Model Mech. 2020. PMID: 32958515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rebholz-Schuhmann D., Kirsch H., Arregui M., Gaudan S., Riethoven M., Stoehr P. EBIMed–text crunching to gather facts for proteins from Medline. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:e237–e244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

