Intracerebral hemorrhage mortality is not changing despite declining incidence
- PMID: 24838789
- PMCID: PMC4113463
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000519
Intracerebral hemorrhage mortality is not changing despite declining incidence
Abstract
Objective: To determine trends in incidence and mortality of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) in a rigorous population-based study.
Methods: We identified all cases of spontaneous ICH in a South Texas community from 2000 to 2010 using rigorous case ascertainment methods within the Brain Attack Surveillance in Corpus Christi Project. Yearly population counts were determined from the US Census, and deaths were determined from state and national databases. Age-, sex-, and ethnicity-adjusted incidence was estimated for each year with Poisson regression, and a linear trend over time was investigated. Trends in 30-day case fatality and long-term mortality (censored at 3 years) were estimated with log-binomial or Cox proportional hazards models adjusted for demographics, stroke severity, and comorbid disease.
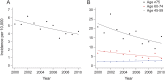
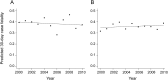
Results: A total of 734 cases of ICH were included. The age-, sex-, and ethnicity-adjusted ICH annual incidence rate was 5.21 per 10,000 (95% confidence interval [CI] 4.36, 6.24) in 2000 and 4.30 per 10,000 (95% CI 3.21, 5.76) in 2010. The estimated 10-year change in demographic-adjusted ICH annual incidence rate was -31% (95% CI -47%, -11%). Yearly demographic-adjusted 30-day case fatality ranged from 28.3% (95% CI 19.9%, 40.3%) in 2006 to 46.5% (95% CI 35.5, 60.8) in 2008. There was no change in ICH case fatality or long-term mortality over time.
Conclusions: ICH incidence decreased over the past decade, but case fatality and long-term mortality were unchanged. This suggests that primary prevention efforts may be improving over time, but more work is needed to improve ICH treatment and reduce the risk of death.
© 2014 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- van Asch CJ, Luitse MJ, Rinkel GJ, van der Tweel I, Algra A, Klijn CJ. Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 2010;9:167–176 - PubMed
-
- Guo F, He D, Zhang W, Walton RG. Trends in prevalence, awareness, management, and control of hypertension among United States adults, 1999 to 2010. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012;60:599–606 - PubMed
-
- Williams LS, Yilmaz EY, Lopez-Yunez AM. Retrospective assessment of initial stroke severity with the NIH Stroke Scale. Stroke 2000;31:858–862 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DC012760/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- K23AG038731/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071759/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23NS073685/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL070941/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R18 HS017690/HS/AHRQ HHS/United States
- R01HL098065/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS044283/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS062675/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS038916/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P20SE01817101/SE/SEPDPO CDC HHS/United States
- K23 NS073685/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS038916/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS38916/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 MD002249/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30ES01788501/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES-021446/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES017885/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS056975/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS070941/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS062675/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL071759/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P60-MD002249/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS070941/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG038731/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01NS073476/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
