Postural alignment in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and its relationship with balance
- PMID: 24838810
- PMCID: PMC4183248
- DOI: 10.1590/s1413-35552012005000152
Postural alignment in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and its relationship with balance
Abstract
Background: In Duchenne muscular dystrophy, functional deficits seem to arise from body misalignment, deconditioning, and obesity secondary to weakness and immobility. The question remains about the effects of postural deviations on the functional balance of these children.
Objectives: To identify and quantify postural deviations in children with DMD in comparison to non-affected children (eutrophic and overweight/obese), exploring relationships between posture and function.
Method: This case-control study evaluated 29 participants aged 6 to 11 years: 10 DMD (DG), 10 eutrophic (EG), and 9 overweight/obese (OG). Digital photogrammetry and SAPo program were used to measure postural alignment and the Pediatric Balance Scale (PBS) was used to measure balance. The Kruskall-Wallis and Dunn post-hoc tests were used for inter-group comparison of posture and balance. Spearman's coefficient tested the correlation between postural and balance variables.
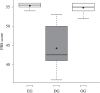
Results: The horizontal pelvic alignment data indicated that the anteversion of the DG was similar to that of the OG and twice that of the EG (p<0.05). Compared to the EG, the DG and OG showed an increased forward position of the center of mass (p<0.05). There was a moderate and weak correlation between the PBS score and horizontal pelvic alignment (0.58 and 0.47-left/right). The PBS showed a weak correlation with asymmetries in the sagittal plane (-0.39). The PBS scores for the OG and EG suggest that obesity did not have a deleterious effect on balance.
Conclusions: The balance deficit in children with DMD was accompanied by an increased forward position of the center of mass and significant pelvic anteversion that constitutes a compensatory strategy to guarantee similar performance to the children not affected by the disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship of body habitus and respiratory function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Respir Med. 2016 Oct;119:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2016.08.018. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Respir Med. 2016. PMID: 27692145
-
Gait deviations in Duchenne muscular dystrophy-Part 2. Statistical non-parametric mapping to analyze gait deviations in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Gait Posture. 2018 Jun;63:159-164. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2018.04.038. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Gait Posture. 2018. PMID: 29751322
-
Effects of functional level on balance in children with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2017 Jul;21(4):635-638. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28259452
-
Anticipatory postural adjustments in a bimanual load-lifting task in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Neurosci Lett. 2006 Aug 7;403(3):271-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.04.054. Epub 2006 Jun 5. Neurosci Lett. 2006. PMID: 16750880
-
Can postural changes in spirometry in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy predict sleep hypoventilation?Paediatr Respir Rev. 2024 Mar;49:9-13. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2023.08.002. Epub 2023 Aug 11. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2024. PMID: 37696714 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between the climbing up and climbing down stairs domain scores on the FES-DMD, the score on the Vignos Scale, age and timed performance of functional activities in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Braz J Phys Ther. 2014 Nov-Dec;18(6):513-20. doi: 10.1590/bjpt-rbf.2014.0063. Braz J Phys Ther. 2014. PMID: 25590443 Free PMC article.
-
Postural control in early stages of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Rev Paul Pediatr. 2025 Jun 27;43:e2024243. doi: 10.1590/1984-0462/2025/43/2024243. eCollection 2025. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40608632 Free PMC article.
-
Lower limb muscle strength is associated with functional performance and quality of life in patients with systemic sclerosis.Braz J Phys Ther. 2015 Mar-Apr;19(2):129-36. doi: 10.1590/bjpt-rbf.2014.0084. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Braz J Phys Ther. 2015. PMID: 25789555 Free PMC article.
-
Postural Control and Sensory Processing in Preschool Children with Autistic Spectrum Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Study.Children (Basel). 2024 Mar 5;11(3):303. doi: 10.3390/children11030303. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539338 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lumbar lordosis increment on gait deteriorations in ambulant boys with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A cross-sectional study.Braz J Phys Ther. 2021 Nov-Dec;25(6):749-755. doi: 10.1016/j.bjpt.2021.05.001. Epub 2021 May 24. Braz J Phys Ther. 2021. PMID: 34119442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kinali M, Main M, Mercuri E, Muntoni F. Evolution of abnormal postures in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2007;10:44–54.
-
- Souza HP. A postura do estudante. Vida e Saúde. 1995:6–7.
-
- Santos NM, Rezende MM, Terni A, Hayashi MCB, Fávero FM, Quadros AAJ, et al. Perfil clínico e funcional dos pacientes com distrofia muscular de Duchenne assistidos na Associação Brasileira de Distrofia Muscular (ABDIM) Rev Neurociênc. 2006;14:15–22.
-
- McDonald CM, Abresch RT, Carter GT, Fowler WM, Johnson ER, Kilmer D, et al. Profiles of neuromuscular diseases. Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1995;74:70–92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00002060-199509001-00003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Okama LO, Queiroz PD, Spina LR, Miranda MBL, Curtarelli MB, Faria M Jr, et al. Avaliação funcional e postural nas distrofias musculares de Duchenne e Becker. ConScientiae Saúde. 2010;9:649–658.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous