Nanosensing at the single cell level
- PMID: 24839348
- PMCID: PMC4022309
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sab.2007.11.027
Nanosensing at the single cell level
Abstract
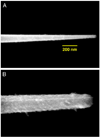
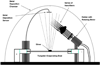
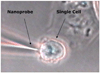
This article presents an overview of the development, operation, and applications of optical nanobiosensors for use in in vivo detection of biotargets in individual living cells. The nanobiosensors are equipped with immobilized bioreceptor probes (e.g., antibodies, enzyme substrate) selective to specific molecular targets. Laser excitation is transmitted into the fiber producing an evanescent field at the tip of the fiber in order to excite target molecules bound to the bioreceptors immobilized at the fiber tips. A photometric system detects the optical signal (e.g., fluorescence) originated from the analyte molecules or from the analyte-bioreceptor reaction. Examples of detection of biospecies and molecular signaling pathways of apoptosis in a living cell are discussed to illustrate the potential of the nanobiosensor technology for single cell analysis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Benzopyrene tetrol; Biosensor; Nanobiosensor; Single cell.
Figures

References
-
- Zandonella C. Cell nanotechnology: the tiny toolkit. Nature. 2003;423:10–12. - PubMed
-
- Vo-Dinh T, Tromberg BJ, Griffin GD, Ambrose KR, Sepaniak, Gardenshire EM. Antibody-based fiberoptics biosensor for the carcinogen benzo(a)pyrene. Appl. Spectrosc. 1987;41:735–739.
-
- Vo-Dinh T, Griffin GD, Sepaniak MJ. Fiberoptics immunosensors. In: Wolfbeis OS, editor. Chemical Sensors and Biosensors. Vol. 2. Florida: CRC Press Boca Raton; 1991. pp. 218–248.
-
- Vo-Dinh T, Sepaniak MJ, Griffin GD, Alarie JP. Immunosensors: principles and applications. Immunomethods. 1993;3:85–93.
-
- Alarie JP, Vo-Dinh T. Antibody-based submicron biosensor for benzo[a] pyrene DNA adduct. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 1996;8:45–52.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
