Deregulation of miR-146a expression in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer affecting EGFR signaling
- PMID: 24839931
- PMCID: PMC4115205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.05.013
Deregulation of miR-146a expression in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer affecting EGFR signaling
Abstract
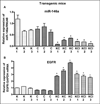
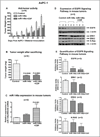
Aberrant expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) plays important roles in the development and progression of pancreatic cancer (PC). Expression analysis of miR-146a in human PC tissues showed decreased expression in about 80% of samples compared to corresponding non-cancerous tissue. Moreover, expression of miR-146a in eight PC cell lines, and in pancreatic tissues obtained from transgenic mouse models of K-Ras (K), Pdx1-Cre (C), K-Ras;Pdx1-Cre (KC) and K-Ras;Pdx1-Cre;INK4a/Arf (KCI), showed down-regulation of miR-146a expression in KCI mice which was in part led to over-expression of its target gene, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Treatment of PC cells with CDF, a novel synthetic compound, led to re-expression of miR-146a, resulting in the down-regulation of EGFR expression. Moreover, re-expression of miR-146a by stable transfection or treatment with CDF in vivo (xenograft animal model) resulted in decreased tumor growth which was consistent with reduced EGFR, ERK1, ERK2, and K-Ras expression. Further knock-down of miR-146a in AsPC-1 cells led to the up-regulation of EGFR expression and showed increased clonogenic growth. In addition, knock-down of EGFR by EGFR siRNA transfection of parental AsPC-1 cells and AsPC-1 cells stably transfected with pre-miR-146a resulted in decreased invasive capacity, which was further confirmed by reduced luciferase activity in cells transfected with pMIR-Luc reporter vector containing miR-146a binding site. Collectively, these results suggest that the loss of expression of miR-146a is a fundamental mechanism for over-expression of EGFR signaling and that re-expression of miR-146a by CDF treatment could be useful in designing personalized strategy for the treatment of human PC.
Keywords: CDF; EGFR; Pancreatic cancer; Xenograft mouse model; miR-146a.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no competing conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inactivation of Ink4a/Arf leads to deregulated expression of miRNAs in K-Ras transgenic mouse model of pancreatic cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Oct;227(10):3373-80. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24036. J Cell Physiol. 2012. Retraction in: J Cell Physiol. 2016 Oct;231(10):2303. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25416. PMID: 22213426 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Anti-tumor activity of a novel compound-CDF is mediated by regulating miR-21, miR-200, and PTEN in pancreatic cancer.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 9;6(3):e17850. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017850. PLoS One. 2011. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2018 Oct 2;13(10):e0205300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205300. PMID: 21408027 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
MicroRNA-146a inhibits glioma development by targeting Notch1.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Sep;31(17):3584-92. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05821-11. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21730286 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA regulation of K-Ras in pancreatic cancer and opportunities for therapeutic intervention.Semin Cancer Biol. 2019 Feb;54:63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.020. Epub 2017 Dec 2. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019. PMID: 29199014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient roles of miR-146a in cellular and molecular mechanisms of neuroinflammatory disorders: An effectual review in neuroimmunology.Immunol Lett. 2021 Oct;238:1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2021.07.004. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Immunol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34293378 Review.
Cited by
-
The miRacle in Pancreatic Cancer by miRNAs: Tiny Angels or Devils in Disease Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 26;17(6):809. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060809. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27240340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives for synthetic curcumins in chemoprevention and treatment of cancer: An update with promising analogues.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 5;906:174266. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174266. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34146588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of resveratrol, curcumin, berberine and other nutraceuticals on aging, cancer development, cancer stem cells and microRNAs.Aging (Albany NY). 2017 Jun 12;9(6):1477-1536. doi: 10.18632/aging.101250. Aging (Albany NY). 2017. PMID: 28611316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-146a suppresses tumor malignancy via targeting vimentin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells with lower fibronectin membrane assembly.J Biomed Sci. 2020 Nov 28;27(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00693-4. J Biomed Sci. 2020. PMID: 33248456 Free PMC article.
-
PTTG1 regulated by miR-146a-3p promotes bladder cancer migration, invasion, metastasis and growth.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 3;8(1):664-678. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13507. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27893422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

