Serine protease inhibition attenuates rIL-12-induced GZMA activity and proinflammatory events by modulating the Th2 profile from estrogen-treated mice
- PMID: 24840346
- PMCID: PMC4097994
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2014-1045
Serine protease inhibition attenuates rIL-12-induced GZMA activity and proinflammatory events by modulating the Th2 profile from estrogen-treated mice
Abstract
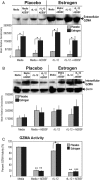
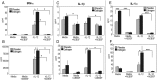
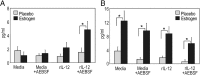
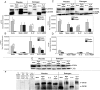
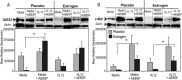
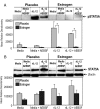
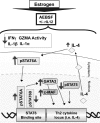
Estrogen has potent immunomodulatory effects on proinflammatory responses, which can be mediated by serine proteases. We now demonstrate that estrogen increased the extracellular expression and IL-12-induced activity of a critical member of serine protease family Granzyme A, which has been shown to possess a novel inflammatory persona. The inhibition of serine protease activity with inhibitor 4-(2-aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride significantly diminished enhanced production of proinflammatory interferon-γ, IL-1β, IL-1α, and Granzyme A activity even in the presence of a Th1-inducing cytokine, IL-12 from splenocytes from in vivo estrogen-treated mice. Inhibition of serine protease activity selectively promoted secretion of Th2-specific IL-4, nuclear phosphorylated STAT6A, signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)6A translocation, and STAT6A DNA binding in IL-12-stimulated splenocytes from estrogen-treated mice. Inhibition with 4-(2-aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride reversed the down-regulation of Th2 transcription factors, GATA3 and c-Maf in splenocytes from estrogen-exposed mice. Although serine protease inactivation enhanced the expression of Th2-polarizing factors, it did not reverse estrogen-modulated decrease of phosphorylated STAT5, a key factor in Th2 development. Collectively, data suggest that serine protease inactivity augments the skew toward a Th2-like profile while down-regulating IL-12-induced proinflammatory Th1 biomolecules upon in vivo estrogen exposure, which implies serine proteases as potential regulators of inflammation. Thus, these studies may provide a potential mechanism underlying the immunomodulatory effect of estrogen and insight into new therapeutic strategies for proinflammatory and female-predominant autoimmune diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serine protease inhibitor, 4-(2-aminoethyl)-benzene sulfonyl fluoride, impairs IL-12-induced activation of pSTAT4β, NFκB, and select pro-inflammatory mediators from estrogen-treated mice.Immunobiology. 2011 Dec;216(12):1264-73. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2011.07.003. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Immunobiology. 2011. PMID: 21813204
-
PI3K and ERK1/2 kinase inhibition potentiate protease inhibitor to attenuate allergen induced Th2 immune response in mouse.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Apr 5;776:176-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.02.050. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26905476
-
Ectopic expression of activated Stat6 induces the expression of Th2-specific cytokines and transcription factors in developing Th1 cells.Immunity. 1999 Dec;11(6):677-88. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80142-9. Immunity. 1999. PMID: 10626890
-
GATA-3 promotes Th2 responses through three different mechanisms: induction of Th2 cytokine production, selective growth of Th2 cells and inhibition of Th1 cell-specific factors.Cell Res. 2006 Jan;16(1):3-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310002. Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16467870 Review.
-
Estrogen, a double-edged sword: modulation of TH1- and TH2-mediated inflammations by differential regulation of TH1/TH2 cytokine production.Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2004 Mar;3(1):97-104. doi: 10.2174/1568010043483944. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2004. PMID: 15032646 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of GZMA as a target of cysteine and biomarker in Alzheimer's disease, pelvic organ prolapse, and tumor progression.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 20;15:1447605. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1447605. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39228516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 1.Rider V, Abdou NI. Gender differences in autoimmunity: molecular basis for estrogen effects in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Immunopharmacol. 2001;1:1009–1024 - PubMed
-
- Cutolo M, Sulli A, Capellino S, et al. Sex hormones influence on the immune system: basic and clinical aspects in autoimmunity. Lupus. 2004;13:635–638 - PubMed
-
- Karpuzoglu-Sahin E, Zhi-Jun Y, Lengi A, Sriranganathan N, Ansar Ahmed S. Effects of long-term estrogen treatment on IFN-γ, IL-2 and IL-4 gene expression and protein synthesis in spleen and thymus of normal C57BL/6 mice. Cytokine. 2001;14:208–217 - PubMed
-
- Maret A, Coudert JD, Garidou L, et al. Estradiol enhances primary antigen-specific CD4 T cell responses and Th1 development in vivo. Essential role of estrogen receptor α expression in hematopoietic cells. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33:512–521 - PubMed
-
- Karpuzoglu E, Zouali M. The multi-faceted influences of estrogen on lymphocytes: toward novel immuno-interventions strategies for autoimmunity management. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011;40:16–26 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

