Consistency Between Treponema pallidum Particle Agglutination Assay and Architect Chemiluminescent Microparticle Immunoassay and Characterization of Inconsistent Samples
- PMID: 24840601
- PMCID: PMC6807155
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21765
Consistency Between Treponema pallidum Particle Agglutination Assay and Architect Chemiluminescent Microparticle Immunoassay and Characterization of Inconsistent Samples
Abstract
Background: Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay (TPPA) has been shown to be highly sensitive and specific at detecting treponemal antibodies and is still used as a confirmatory method in many laboratories, in China. In clinical practice, we found that a significant number of TPPA-negative sera were identified when TPPA was used as a confirmatory assay of Architect chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) screening-reactive sera.
Aims: To investigate the consistency between Architect CMIA and TPPA, and analyzed the characterization of TPPA-negative sera following Screening by Architect CMIA.
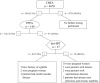
Methods: According to the laboratory syphilis confirmatory testing protocol, a total of 4870 sera were initially tested by Architect CMIA and ELISA, and then the samples which shown positive results were tested by TPPA and rapid plasma reagin tests (RPR). Further analysis using Euroimmun dot-immunoblot (dot-IBT) assay was performed to the CMIA positive and TPPA negative samples.
Results: In our cohort, we found that the positive rate of CMIA was 3.1% (149/4870). One hundred and twelve of 112 (75.2%) CMIA-positive sera were TPPA reactive, while 37 (24.8%) sera which were reactive in CMIA were nonreactive by TPPA. Dot-IBT testing was performed on these 37 sera: 8 (21.6%) were dot-IBT positive, 11 (29.7%) were indeterminate and 18 (48.6%) negative.
Discussion: In this study, we observed that 18 CMIA-positive sera were false positives confirmed by dot-IBT. But, given the relatively high levels of early syphilis, we consider a small increase in the number of confirmatory tests is worthwhile if we can increase the detection of primary syphilis by 20%. We also found that significant numbers (8/37) of CMIA-positive and TPPA-negative sera were shown by further dot-IBT testing to be positive. The reason why certain sera are negative by TPPA but reactive by CMIA and other syphilis confirmatory assays is not clear, and these initial findings should be further explored.
Conclusion: The Architect CMIA is a highly sensitive screening assay for detecting syphilis but it is significantly less specific. Further analysis by TPPA is recommended to confirm the results. We would highlight the fact that in repeatedly screened populations discrepancies between treponemal CMIA and TPPA results are quite prevalent. This seems to be a function of very low levels of syphilis-specific antibodies. Confirmation by immunoblot assay may be useful.
Keywords: Treponema pallidum; screening; serological test; syphilis.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison and evaluation of Abbott chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay and ChIVD light-initiated chemiluminescent assay in the detection of Treponema pallidum antibody.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jul;34(7):e23275. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23275. Epub 2020 Mar 4. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32133697 Free PMC article.
-
Modified TPPA combined with western blotting facilitates syphilis diagnosis in isolated reactive treponemal chemiluminescence immunoassay sera: a prospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jan 2;25(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10404-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39748275 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for antibodies against Treponema pallidum with chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay: analysis of discordant serology results and clinical characterization.Ann Clin Biochem. 2016 Sep;53(Pt 5):588-92. doi: 10.1177/0004563215623806. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Ann Clin Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26680646
-
[Recent Advances in Laboratory Diagnosis of Syphilis].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2023 Jan;57(1):141-155. doi: 10.5578/mb.20239912. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2023. PMID: 36636853 Review. Turkish.
-
The Laboratory Diagnosis of Syphilis.J Clin Microbiol. 2021 Sep 20;59(10):e0010021. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00100-21. Epub 2021 May 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33980644 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Confirmation value of Western blotting in detecting anti-treponema pallidum specific antibodies with suspicious results.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Feb 2;27(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00633-y. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35109919 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison and evaluation of Abbott chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay and ChIVD light-initiated chemiluminescent assay in the detection of Treponema pallidum antibody.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jul;34(7):e23275. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23275. Epub 2020 Mar 4. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32133697 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of "Lumipulse anti-Treponema pallidum" and "Architect Syphilis TP" and further examination.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 May;34(5):e23194. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23194. Epub 2020 Jan 24. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31981241 Free PMC article.
-
Modified TPPA combined with western blotting facilitates syphilis diagnosis in isolated reactive treponemal chemiluminescence immunoassay sera: a prospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jan 2;25(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10404-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39748275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen MS, Henderson GE, Aiello P, et al. Successful eradication of sexually transmitted diseases in the People's Republic of China: Implications for the 21st century. J Infect Dis 1996;174(Suppl 2):S223–S229. - PubMed
-
- Aktas G, Young H, Moyes A, et al. Evaluation of the Serodia Treponema pallidum particle agglutination, the Murex Syphilis ICE and the Enzywell TP tests for serodiagnosis of syphilis. Int J STD AIDS 2005;16:294–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources