Chemoselective amination of propargylic C(sp³)-H bonds by cobalt(II)-based metalloradical catalysis
- PMID: 24840605
- PMCID: PMC4119425
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201400557
Chemoselective amination of propargylic C(sp³)-H bonds by cobalt(II)-based metalloradical catalysis
Abstract
Highly chemoselective intramolecular amination of propargylic C(sp(3))-H bonds has been demonstrated for N-bishomopropargylic sulfamoyl azides through cobalt(II)-based metalloradical catalysis. Supported by D(2h)-symmetric amidoporphyrin ligand 3,5-Di(t)Bu-IbuPhyrin, the cobalt(II)-catalyzed C-H amination proceeds effectively under neutral and nonoxidative conditions without the need of any additives, and generates N2 as the only byproduct. The metalloradical amination is suitable for both secondary and tertiary propargylic C-H substrates with an unusually high degree of functional-group tolerance, thus providing a direct method for high-yielding synthesis of functionalized propargylamine derivatives.
Keywords: alkynes; chemoselectivity; cobalt; heterocycles; homogeneous catalysis.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
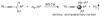

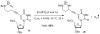
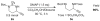
Similar articles
-
Catalytic Radical Process for Enantioselective Amination of C(sp3 )-H Bonds.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Dec 17;57(51):16837-16841. doi: 10.1002/anie.201808923. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 30347505 Free PMC article.
-
Intramolecular 1,5-C(sp3)-H Radical Amination via Co(II)-Based Metalloradical Catalysis for Five-Membered Cyclic Sulfamides.Chem Sci. 2016;7(12):6934-6939. doi: 10.1039/C6SC02231F. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Chem Sci. 2016. PMID: 28138382 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Radical Amination of Aldehydic C(sp2)-H Bonds with Fluoroaryl Azides via Co(II)-Based Metalloradical Catalysis: Synthesis of N-Fluoroaryl Amides from Aldehydes under Neutral and Nonoxidative Conditions.Chem Sci. 2014 Jun 1;5(6):2422-2427. doi: 10.1039/C4SC00697F. Chem Sci. 2014. PMID: 25071929 Free PMC article.
-
Direct addition of alkynes to imines and related C=N electrophiles: A convenient access to propargylamines.Chem Commun (Camb). 2006 Nov 4;(41):4263-75. doi: 10.1039/b607986p. Epub 2006 Aug 25. Chem Commun (Camb). 2006. PMID: 17047838 Review.
-
The Asymmetric A³(Aldehyde⁻Alkyne⁻Amine) Coupling: Highly Enantioselective Access to Propargylamines.Molecules. 2019 Mar 28;24(7):1216. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071216. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30925732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stereoretentive and regioselective selenium-catalyzed intermolecular propargylic C-H amination of alkynes.Chem Sci. 2022 Jan 27;13(7):2121-2127. doi: 10.1039/d1sc07067c. eCollection 2022 Feb 16. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35308840 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the Electronic Structure of Cobalt Porphyrin Nitrene and Carbene Radicals with NEVPT2-CASSCF Calculations: Doublet versus Quartet Ground States.Inorg Chem. 2021 Jun 21;60(12):8380-8387. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c00910. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Inorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34096281 Free PMC article.
-
Copper-catalyzed direct transformation of simple alkynes to alkenyl nitriles via aerobic oxidative N-incorporation.Chem Sci. 2015 Nov 1;6(11):6355-6360. doi: 10.1039/c5sc02126j. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 30090253 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into cobalt(ii/iii)-catalyzed C-H oxidation: a combined theoretical and experimental study.Chem Sci. 2015 Dec 1;6(12):7059-7071. doi: 10.1039/c5sc01807b. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 29861945 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of dienes from pyrrolidines using skeletal modification.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 11;14(1):7307. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43238-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37951966 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Selected examples: Nilsson B, Vargas HM, Ringdahl B, Hacksell U. J Med Chem. 1992;35:285–294.Jenmalm A, Berts W, Li YL, Luthman K, Csoeregh I, Hacksell U. J Org Chem. 1994;59:1139–1148.Miura M, Enna M, Okuro K, Nomura M. J Org Chem. 1995;60:4999–5004.Davidson MH, McDonald FE. Org Lett. 2004;6:1601–1603.Trost BM, Chung CK, Pinkerton AB. Angew Chem. 2004;116:4427–4429.Angew Chem Int Ed. 2004;43:4327–4329.Nakamura H, Kamakura T, Ishikura M, Biellmann JF. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:5958–5959.Detz RJ, Abiri Z, le Griel R, Hiemstra H, van Maarseveen JH. Chem Eur J. 2011;17:5921–5930.Ding CH, Hou XL. Chem Rev. 2011;111:1914–1937.Aubert C, Buisine O, Malacria M. Chem Rev. 2002;102:813–834.Naota T, Takaya H, Murahashi SI. Chem Rev. 1998;98:2599–2660.
-
-
- Konishi M, Ohkuma H, Tsuno T, Oki T, Vanduyne GD, Clardy J. J Am Chem Soc. 1990;112:3715–3716.
- Yu PH, Davis BA, Boulton AA. J Med Chem. 1992;35:3705–3713. - PubMed
- Huffman MA, Yasuda N, Decamp AE, Grabowski EJJ. J Org Chem. 1995;60:1590–1594.
- Enders D, Reinhold U. Tetrahedron-Asymmetry. 1997;8:1895–1946.
- Kauffman GS, Harris GD, Dorow RL, Stone BRP, Parsons RL, Pesti JA, Magnus NA, Fortunak JM, Confalone PN, Nugent WA. Org Lett. 2000;2:3119–3121. - PubMed
-
- Aubrecht KB, Winemiller MD, Collum DB. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:11084–11089.
- Tuulmets A, Pallin V, Tammiku-Taul J, Burk P, Raie K. J Phys Org Chem. 2002;15:701–705.
- Murai T, Ohta Y, Mutoh Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005;46:3637–3640.
- Ma Y, Lobkovsky E, Collum DB. J Org Chem. 2005;70:2335–2337. - PubMed
- Magueur G, Crousse B, Bonnet-Delpon D. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005;46:2219–2221.
- Ding CH, Chen DD, Luo ZB, Dai LX, Hou XL. Synlett. 2006:1272–1274.
- Badorrey R, Diaz-de-Villegas MD, Diez R, Galvez JA. Eur J Org Chem. 2007:2114–2120.
- Wee AGH, Zhang B. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007;48:4135–4138.
-
-
For recent reviews on “A3-coupling”, see: Peshkov VA, Pereshivko OP, Van der Eycken EV. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41:3790–3807.Yoo WJ, Zhao L, Li CJ. Aldrichimica Acta. 2011;44:43–51.Li CJ. Acc Chem Res. 2010;43:581–590.Kouznetsov VV, Méndez LYV. Synthesis. 2008;4:491–506.Zani L, Bolm C. Chem Commun. 2006:4263–4275.Wei CM, Li ZG, Li CJ. Synlett. 2004:1472–1483.
-
-
-
For synthesis of propargylamines through alkynylation of C–H bonds adjacent to nitrogen atoms of existing amines, see: Li ZP, Li CJ. Org Lett. 2004;6:4997–4999.Li ZP, Li CJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:11810–11811.Niu M, Yin Z, Fu H, Jiang Y, Zhao Y. J Org Chem. 2008;73:3961–3963.Detz RJ, Abiri Z, le Griel R, Hiemstra H, van Maarseveen JH. Chem-Eur J. 2011;17:5921–5930.Sugiishi T, Nakamura H. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:2504–2507.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

