Alternative splicing and highly variable cadherin transcripts associated with field-evolved resistance of pink bollworm to bt cotton in India
- PMID: 24840729
- PMCID: PMC4026531
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097900
Alternative splicing and highly variable cadherin transcripts associated with field-evolved resistance of pink bollworm to bt cotton in India
Abstract
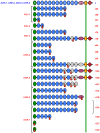
Evolution of resistance by insect pests can reduce the benefits of insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) that are used extensively in sprays and transgenic crops. Despite considerable knowledge of the genes conferring insect resistance to Bt toxins in laboratory-selected strains and in field populations exposed to Bt sprays, understanding of the genetic basis of field-evolved resistance to Bt crops remains limited. In particular, previous work has not identified the genes conferring resistance in any cases where field-evolved resistance has reduced the efficacy of a Bt crop. Here we report that mutations in a gene encoding a cadherin protein that binds Bt toxin Cry1Ac are associated with field-evolved resistance of pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) in India to Cry1Ac produced by transgenic cotton. We conducted laboratory bioassays that confirmed previously reported resistance to Cry1Ac in pink bollworm from the state of Gujarat, where Bt cotton producing Cry1Ac has been grown extensively. Analysis of DNA from 436 pink bollworm from seven populations in India detected none of the four cadherin resistance alleles previously reported to be linked with resistance to Cry1Ac in laboratory-selected strains of pink bollworm from Arizona. However, DNA sequencing of pink bollworm derived from resistant and susceptible field populations in India revealed eight novel, severely disrupted cadherin alleles associated with resistance to Cry1Ac. For these eight alleles, analysis of complementary DNA (cDNA) revealed a total of 19 transcript isoforms, each containing a premature stop codon, a deletion of at least 99 base pairs, or both. Seven of the eight disrupted alleles each produced two or more different transcript isoforms, which implicates alternative splicing of messenger RNA (mRNA). This represents the first example of alternative splicing associated with field-evolved resistance that reduced the efficacy of a Bt crop.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Similar genetic basis of resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in Boll-selected and diet-selected strains of pink bollworm.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035658. Epub 2012 Apr 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22530065 Free PMC article.
-
A long non-coding RNA regulates cadherin transcription and susceptibility to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2019 Jul;158:54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2019.04.007. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31378361
-
Responses to Bt toxin Vip3Aa by pink bollworm larvae resistant or susceptible to Cry toxins.Pest Manag Sci. 2022 Oct;78(10):3973-3979. doi: 10.1002/ps.7016. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Pest Manag Sci. 2022. PMID: 35633103
-
Early detection of field-evolved resistance to Bt cotton in China: cotton bollworm and pink bollworm.J Invertebr Pathol. 2012 Jul;110(3):301-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 Apr 16. J Invertebr Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22537835 Review.
-
Sustained susceptibility of pink bollworm to Bt cotton in the United States.GM Crops Food. 2012 Jul-Sep;3(3):194-200. doi: 10.4161/gmcr.20329. Epub 2012 Jul 1. GM Crops Food. 2012. PMID: 22572905 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of a Transcriptome in a Model Lepidopteran Pest, Heliothis virescens, Using Multiple Sequencing Strategies for Profiling Midgut Gene Expression.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):e0128563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128563. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26047101 Free PMC article.
-
Fitness costs of resistance to insecticides in insects.Front Physiol. 2023 Oct 19;14:1238111. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1238111. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37929209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequencing, de novo assembly and annotation of a pink bollworm larval midgut transcriptome.Gigascience. 2016 Jun 22;5:28. doi: 10.1186/s13742-016-0130-9. Gigascience. 2016. PMID: 27333791 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional analysis of susceptible and resistant European corn borer strains and their response to Cry1F protoxin.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jul 29;16(1):558. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1751-6. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26220297 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the resistance to Vip3Aa in Helicoverpa armigera from Australia and the role of midgut processing and receptor binding.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 20;6:24311. doi: 10.1038/srep24311. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27095284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendelsohn M, Kough J, Vaituzis Z, Matthews K (2003) Are Bt crops safe? Nat Biotechnol 21: 1003–1009. - PubMed
-
- Sanahuja G, Banakar R, Twyman RM, Capell T, Christou P (2011) Bacillus thuringiensis: A century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol J 9: 283–300. - PubMed
-
- James C (2013) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops: 2013. ISAAA Briefs No. 46. ISAAA: Ithaca, NY.
-
- Wu KM, Lu YH, Feng HQ, Jiang YY, Zhao JZ (2008) Suppression of cotton bollworm in multiple crops in China in areas with Bt toxin-containing cotton. Science 321: 1676–1678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

