Evaluation of four different analytical tools to determine the regional origin of Gastrodia elata and Rehmannia glutinosa on the basis of metabolomics study
- PMID: 24840900
- PMCID: PMC6271526
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19056294
Evaluation of four different analytical tools to determine the regional origin of Gastrodia elata and Rehmannia glutinosa on the basis of metabolomics study
Abstract
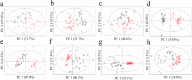
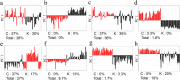
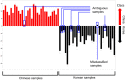
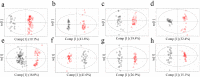
Chemical profiles of medicinal plants could be dissimilar depending on the cultivation environments, which may influence their therapeutic efficacy. Accordingly, the regional origin of the medicinal plants should be authenticated for correct evaluation of their medicinal and market values. Metabolomics has been found very useful for discriminating the origin of many plants. Choosing the adequate analytical tool can be an essential procedure because different chemical profiles with different detection ranges will be produced according to the choice. In this study, four analytical tools, Fourier transform near‑infrared spectroscopy (FT-NIR), 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H‑NMR), liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), and gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) were applied in parallel to the same samples of two popular medicinal plants (Gastrodia elata and Rehmannia glutinosa) cultivated either in Korea or China. The classification abilities of four discriminant models for each plant were evaluated based on the misclassification rate and Q2 obtained from principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal projection to latent structures-discriminant analysis (OPLS‑DA), respectively. 1H-NMR and LC-MS, which were the best techniques for G. elata and R. glutinosa, respectively, were generally preferable for origin discrimination over the others. Reasoned by integrating all the results, 1H-NMR is the most prominent technique for discriminating the origins of two plants. Nonetheless, this study suggests that preliminary screening is essential to determine the most suitable analytical tool and statistical method, which will ensure the dependability of metabolomics-based discrimination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discrimination of Gastrodia elata from Different Geographical Origin for Quality Evaluation Using Newly-Build Near Infrared Spectrum Coupled with Multivariate Analysis.Molecules. 2018 May 4;23(5):1088. doi: 10.3390/molecules23051088. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29734695 Free PMC article.
-
Specific targeted quantification combined with non-targeted metabolite profiling for quality evaluation of Gastrodia elata tubers from different geographical origins and cultivars.J Chromatogr A. 2016 Jun 10;1450:53-63. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2016.04.077. Epub 2016 Apr 29. J Chromatogr A. 2016. PMID: 27157425
-
Metabolomics approach for the discrimination of raw and steamed Gastrodia elata using liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jun;94:132-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.01.032. Epub 2014 Jan 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 24561339
-
Screening of synthetic PDE-5 inhibitors and their analogues as adulterants: analytical techniques and challenges.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;87:176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.037. Epub 2013 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 23721687 Review.
-
Hyphenated techniques and their applications in natural products analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;864:301-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-624-1_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22367902 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimal Extraction Study of Gastrodin-Type Components from Gastrodia Elata Tubers by Response Surface Design with Integrated Phytochemical and Bioactivity Evaluation.Molecules. 2019 Feb 2;24(3):547. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030547. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30717352 Free PMC article.
-
Application for Identifying the Origin and Predicting the Physiologically Active Ingredient Contents of Gastrodia elata Blume Using Visible-Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning.Foods. 2023 Nov 8;12(22):4061. doi: 10.3390/foods12224061. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38002117 Free PMC article.
-
Near-Infrared Spectroscopy as a Process Analytical Technology Tool for Monitoring the Steaming Process of Gastrodiae rhizoma with Multiparameters and Chemometrics.J Anal Methods Chem. 2020 Nov 4;2020:8847277. doi: 10.1155/2020/8847277. eCollection 2020. J Anal Methods Chem. 2020. PMID: 33204575 Free PMC article.
-
Discrimination of Gastrodia elata from Different Geographical Origin for Quality Evaluation Using Newly-Build Near Infrared Spectrum Coupled with Multivariate Analysis.Molecules. 2018 May 4;23(5):1088. doi: 10.3390/molecules23051088. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29734695 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison on Bioactivities and Characteristics of Polysaccharides From Four Varieties of Gastrodia elata Blume.Front Chem. 2022 Jul 22;10:956724. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.956724. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35936076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guerra M.C., Speroni E., Broccoli M., Cangini M., Pasini P., Minghetti A., Crespi-Perellino N., Mirasoli M., Cantelli-Forti G., Paolini M. Comparison between Chinese medical herb Pueraria lobata crude extract and its main isoflavone puerarin: Antioxidant properties and effects on rat liver CYP-catalysed drug metabolism. Life Sci. 2000;67:2997–3006. doi: 10.1016/S0024-3205(00)00885-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lydon J., Duke S.O. Pesticide effects on secondary metabolism of higher plants. Pest. Sci. 1989;25:361–373. doi: 10.1002/ps.2780250406. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

