"Slow VISA," a novel phenotype of vancomycin resistance, found in vitro in heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus strain Mu3
- PMID: 24841271
- PMCID: PMC4135821
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02470-13
"Slow VISA," a novel phenotype of vancomycin resistance, found in vitro in heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus strain Mu3
Abstract
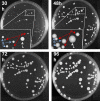
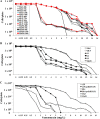
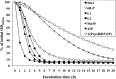
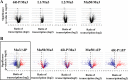
Heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (hVISA) clinical strain Mu3 spontaneously generates VISA strains at an extremely high frequency (≥1×10(-6)). The generated VISA strains usually grow more slowly than does the parent hVISA strain, but they form colonies on vancomycin-containing agar plates before 48 h of incubation. However, we noticed a curious group of VISA strains, designated "slow VISA" (sVISA), whose colonies appear only after 72 h of incubation. They have extremely prolonged doubling times but have vancomycin MICs of 8 to ∼24 mg/liter when determined after 72 to ∼144 h of incubation. We established strain Mu3-6R-P (6R-P), which has a vancomycin MIC of 16 mg/liter (at 72 h), as a representative sVISA strain. Its cell wall was thickened and autolytic activity was decreased compared to the respective qualities of the parent hVISA strain Mu3. Whole-genome sequencing of 6R-P revealed only one mutation, encoded by rpoB (R512P), which replaced the 512th arginine of the RNA polymerase β-subunit with proline. Its VISA phenotype was unstable, and the strain frequently reverted to hVISA with concomitant losses of pinpoint colony morphology and cell wall thickness and reduced autolytic activity. Sequencing of the rpoB genes of the phenotypic revertant strains revealed mutations affecting the 512th codon, where the proline of 6R-P was replaced with leucine, serine, or histidine. Slow VISA generated in the tissues of an infected patient serves as a temporary shelter for hVISA to survive vancomycin therapy. The sVISA strain spontaneously returns to hVISA when the threat of vancomycin is lifted. The rpoB(R512P) mutation may be regarded as a regulatory mutation that switches the reversible phenotype of sVISA on and off.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Neoh HM, Cui L, Yuzawa H, Takeuchi F, Matsuo M, Hiramatsu K. 2008. Mutated response regulator graR is responsible for phenotypic conversion of Staphylococcus aureus from heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate resistance to vancomycin-intermediate resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52:45–53. 10.1128/AAC.00534-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matsuo M, Cui L, Kim J, Hiramatsu K. 2013. Comprehensive identification of mutations responsible for heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (hVISA)-to-VISA conversion in laboratory-generated VISA strains from hVISA clinical strain Mu3. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57:5843–583. 10.1128/AAC.00425-13 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

