Characterization of a novel and potentially lethal designer drug (±)-cis-para-methyl-4-methylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR, or 'Serotoni')
- PMID: 24841869
- PMCID: PMC4128571
- DOI: 10.1002/dta.1668
Characterization of a novel and potentially lethal designer drug (±)-cis-para-methyl-4-methylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR, or 'Serotoni')
Abstract
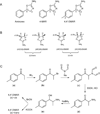
During the second half of 2013, a total of 26 deaths involving para-methyl-4-methylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR) were reported to the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. While aminorex and 4-methylaminorex (4-MAR) are known psychostimulants, nothing is known about the comparatively new para-methyl analog. Analytical characterization of two independent samples obtained from online vendors confirmed the presence of the (±)-cis isomer that also appeared to be associated with at least 18 of the 26 deaths. Extensive characterizations included crystal structure analysis, single, tandem, and high-resolution mass spectrometry, liquid and gas chromatography, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. For the work described here, both the (±)-cis and (±)-trans racemates were also synthesized, confirming that the differentiation between these two forms was straight-forward. Monoamine transporter activity was studied using rat brain synaptosomes which included the comparison with d-amphetamine, aminorex and (±)-cis-4-MAR. (±)-cis-4,4'-DMAR was a potent, efficacious substrate-type releaser at transporters for dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin with EC50 values of 8.6 ± 1.1 nM (DAT), 26.9 ± 5.9 nM (NET) and 18.5 ± 2.8 nM (SERT), respectively. The potency of (±)-cis-4,4'-DMAR at DAT and NET rivalled that of other psychomotor stimulant drugs like d-amphetamine and aminorex. However, (±)-cis-4,4'-DMAR had much more potent actions at SERT and activity at SERT varied more than 100-fold across the four drugs. The potent releasing activity of (±)-cis-4,4'-DMAR at all three monoamine transporters predicts a potential for serious side-effects such as psychotic symptoms, agitation, hyperthermia and cardiovascular stimulation, especially after high-dose exposure or following combination with other psychostimulants.
Keywords: 4-methylaminorex; Internet; aminorex; monoamine transporters; new psychoactive substances; para-methyl-4-methylaminorex; psychostimulants; synaptosomes.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures






References
-
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) Action on new drugs. [11 March 2014]; Available at: http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/activities/action-on-new-drugs.
-
- EMCDDA-Europol. EU drug markets report: a strategic analysis. Lisbon: EMCDDA; 2013. Jan, [11 March 2014]. Avilable at: http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/publications/joint-publications/drug-markets.
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) A Report from the Global SMART Programme March 2013. Vienna: United Nations Publication; 2013. [11 March 2014]. The challenge of new psychoactive substances. Available at: www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/NPS_2013_SMART.pdf.
-
- Council Decision 2005/387/JHA of 20 May 2005 on the information exchange, risk-assessment and control of new psychoactive substances. Official J. EU. 2005 L 127/32.
-
- Ioannides-Demos LL, Proietto J, Tonkin AM, McNeil JJ. Safety of drug therapies used for weight loss and treatment of obesity. Drug Saf. 2006;29:277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

