Written emotional disclosure for asthma
- PMID: 24842151
- PMCID: PMC11254376
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007676.pub2
Written emotional disclosure for asthma
Abstract
Background: Psychological stress has been widely implicated in asthma exacerbation. Evidence suggests that written emotional disclosure, an intervention that involves writing about traumatic or stressful experiences, helps to reduce stress and promote physical and psychological well-being. Written emotional disclosure may have a role in the management of asthma.
Objectives: This review aims to determine the effectiveness of written emotional disclosure for people with asthma, specifically, to assess:1. overall efficacy of emotional disclosure compared with emotionally neutral writing on self reported quality of life in people with asthma;2. overall efficacy of emotional disclosure compared with emotionally neutral writing on objective measures of health outcome in people with asthma; and3. comparative efficacy of different types of emotional disclosure for people with asthma.
Search methods: Trials were identified from the Cochrane Airways Group Specialised Register of trials, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, AMED and PsycINFO. The latest search was conducted in January 2014.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials published in any language comparing written emotional disclosure intervention versus a control writing (emotionally neutral) intervention in participants with asthma were included in the review.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed studies against predetermined inclusion criteria and extracted the data. Corresponding authors were contacted when necessary to provide additional information.
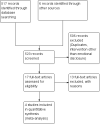
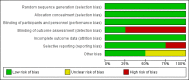
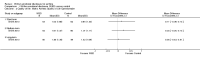
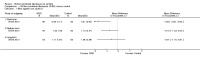
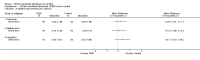
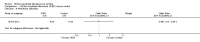
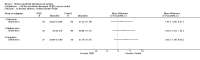
Main results: Four studies, involving a total of 414 participants, met the inclusion criteria. Three studies were conducted in adult participants and one in adolescents. The average age of participants ranged from 14 to 43 years. The trials lasted between two months and 12 months. The interventions were based on Pennebaker's method. The risk of bias across most domains of the studies was generally considered to be low, however three of four studies were considered at high risk of bias due to lack of assessor blinding and one study was at high risk of bias for selective reporting. The interpretation of these studies was limited by diverse outcome measurements, measurement tools, control group techniques, and number and/or times of follow-up. A pooled result from the four studies, including a total of 146 intervention and 135 control participants, indicated uncertain effect in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) % predicted between the disclosure group and the control group (mean difference (MD) 3.43%, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.61% to 7.47%; very low-quality evidence) at ≤ three months' follow-up. Similarly, evidence from two studies indicated that written emotional disclosure found uncertain effect on forced vital capacity (FVC) (standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.02, 95% CI -0.30 to 0.26; low-quality evidence) and asthma symptoms (SMD -0.22, 95% CI -0.52 to 0.09; low-quality evidence) but may result in improved asthma control at ≤ three months' follow-up (SMD 0.29, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.58; low-quality evidence). We were unable to pool the data for other outcomes. Results from individual trials did not reveal a significant benefit of written emotional disclosure for quality of life, medication use, healthcare utilisation or psychological well-being. Evidence from one trial suggests a significant reduction in beta agonist use (MD -1.62, 95% CI -2.62 to -0.62; low-quality evidence) at ≤ three months' follow-up in the disclosure group compared with controls. The review did not address any adverse effects of emotional writing.
Authors' conclusions: Evidence was insufficient to show whether written emotional disclosure compared with writing about non-emotional topics had an effect on the outcomes included in this review. Evidence is insufficient to allow any conclusions as to the role of disclosure in quality of life, psychological well-being, medication use and healthcare utilisation. The evidence presented in this review is generally of low quality. Better designed studies with standardised reporting of outcome measurement instruments are required to determine the effectiveness of written emotional disclosure in the management of asthma.
Conflict of interest statement
HS, CJ, AT and MH were involved in a trial of written emotional disclosure for asthma.
Figures








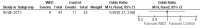






Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007676
Similar articles
-
Psychological therapies for post-traumatic stress disorder and comorbid substance use disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 4;4(4):CD010204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27040448 Free PMC article.
-
Home-based educational interventions for children with asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Feb 6;2(2):CD008469. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008469.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39912443
-
Conservative, physical and surgical interventions for managing faecal incontinence and constipation in adults with central neurological diseases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 29;10(10):CD002115. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002115.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39470206
-
Music-based therapeutic interventions for people with dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Mar 7;3(3):CD003477. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003477.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40049590
-
Mobile phone messaging for facilitating self-management of long-term illnesses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD007459. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007459.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235644 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-pharmacological interventions for asthma prevention and management across the life course: Umbrella review.Clin Transl Allergy. 2024 Mar;14(3):e12344. doi: 10.1002/clt2.12344. Clin Transl Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38423800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of non-drug therapies on asthma control: A systematic review of the literature.Eur J Gen Pract. 2019 Apr;25(2):65-76. doi: 10.1080/13814788.2019.1574742. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Gen Pract. 2019. PMID: 30849253 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol for an HTA report: Does therapeutic writing help people with long-term conditions? Systematic review, realist synthesis and economic modelling.BMJ Open. 2014 Feb 18;4(2):e004377. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004377. BMJ Open. 2014. PMID: 24549165 Free PMC article.
-
Do expressive writing interventions have positive effects on Koreans?: a meta-analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Nov 23;14:1204053. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1204053. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38076691 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Harris 2005 {published data only}
-
- Harris AH, Thoresen CE, Humphreys K, Faul J. Does writing affect asthma? A randomised trial. Psychosomatic Medicine 2006;67(1):130‐6. - PubMed
Smith 2013 {unpublished data only}
-
- Smith H, Hankins H, Jones CJ, Theadom A, Bowskill R, Rob H, Frew A. Does expressive writing improve lung function and quality of life in adults with asthma?. Unpublished manuscript draft. - PubMed
Smyth 1999 {published data only}
-
- Smyth JM, Stone AA, Hurewitz A, Kaell A. Effects of writing about stressful experiences on symptom reduction in patients with asthma or rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised trial. JAMA 1999;281(14):1304‐9. - PubMed
Warner 2006 {published data only}
-
- Warner LJ, Lumley MA, Casey RJ, Pierantoni W, Salazar R, Zoratti EM, et al. Health effects of written emotional disclosure in adolescents with asthma: a randomised, controlled trial. Journal of Padeatric Psychology 2006;31(6):557‐68. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Bruzzese 2011 {published data only}
Hockemeyer 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hockemeyer J, Smyth J. Evaluating the feasibility and efficacy of a self‐administered manual‐based stress management intervention for individuals with asthma: results from a controlled study. Behavioural Medicine 2002;27(4):161‐72. - PubMed
Horowitz 2008 {published data only}
-
- Horowitz S. Evidence‐based health outcomes of expressive writing. Alternative and Complementary Therapies 2008;14(4):194‐8.
Hyland 1993 {published data only}
Magar 2005 {published data only}
-
- Magar Y, Vervloet D, Steenhouwer F, Smaga S, Mechin H, Rocca Serra JP, et al. Assessment of a therapeutic education programme for asthma patients: "un souffle nouveau". Patient Education and Counseling 2005;58(1):41‐6. - PubMed
McGhan 2010 {published data only}
Okelo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Okelo SO, Wu AW, Krishnan JA, Rand CS, Skinner EA, Diette GB. Emotional quality‐of‐life and outcomes in adolescents with asthma. Journal of Paediatrics 2004;145:523‐9. - PubMed
Shah 2001 {published data only}
Sharifabad 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sharifabad MA, Hurewitz A, Spiegler P, Bernstein M, Feuerman M, Smyth JM. Written disclosure therapy for patients with chronic lung disease undergoing pulmonary rehabilitation. Journal of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation and Prevention 2010;30(5):340‐5. - PubMed
Smyth 2002 {published data only}
-
- Smyth J, Anderson C, Hockemeyer J, Stone A. Does emotional non‐expressiveness or avoidance interfere with writing about stressful life events? An analysis in patients with chronic illness. Psychology and Health 2002;17(5):561‐9.
Theadom 2010 {published data only}
-
- Theadom A, Smith H, Horne R, Bowskill R, Apfelbacher CJ, Frew A. Participant experiences of a written emotional disclosure intervention in asthma. Stress and Health 2010;26(1):45‐50.
Tousman 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tousman SA, Zeitz H, Bond D, Stewart D, Rackow R, Greer R, et al. A randomized controlled behavioral trial of a new adult asthma self‐management program. Journal of Asthma and Allergy Educators 2011;2(2):91‐6.
Urek 2005 {published data only}
-
- Urek MC, Tudorić N, Plavec D, Urek R, Koprivc‐Milenović T, Stojić M. Effect of educational programs on asthma control and quality of life in adult asthma patients. Patient Education and Counseling 2005;58(1):47‐74. - PubMed
Additional references
Beasley 2004
-
- Beasley R. The Global Burden of Asthma Report, Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). http://www.ginasthma.org/Global‐Burden‐of‐Asthma (accessed 6 January 2014).
Cohen 1983
-
- Cohen S, Kamarck T, Mermelstein R. A global measure of perceived stress. Journal of Health and Social Behaviour 1983;24(4):385‐96. - PubMed
Frattaroli 2006
-
- Frattaroli J. Experimental disclosure and its moderators: a meta‐analysis. Psychological Bulletin 2006;132(6):823‐65. - PubMed
Frisina 2004
-
- Frisina PG, Borod JC, Lepore SJ. A meta‐analysis of the effects of written emotional disclosure on the health outcomes of clinical populations. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 2004;192(9):629‐34. - PubMed
Gidron 2002
-
- Gidron Y, Duncan E, Lazar A, Biderman A, Tandeter H, Shvartzman P. Effects of guided written disclosure of stressful experiences on clinic visits and symptoms in frequent clinic attenders. Family Practice 2002;19(2):161‐6. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Hyland 1995
-
- Hyland ME, Ley A, Fisher DW, Woodward V. Measurement of psychological distress in asthma and asthma management programmes. British Journal of Clinical Psychology 1995;34(4):601‐11. - PubMed
Juniper 1999
-
- Juniper EF, O'Byrne PM, Guyatt GH, Ferrie PJ, King DR. Development and validation of a questionnaire to measure asthma control. European Respiratory Journal 1999;14(4):902‐7. - PubMed
Lepore 2002
-
- Lepore SJ, Greenberg MA, Bruno M, Smyth JM. Expressive writing and health: self‐regulation of emotion‐related experience, physiology, and behavior. In: Lepore SJ, Smyth JM editor(s). The Writing Cure: How Expressive Writing Promotoes Health and Emotional Well‐Being. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, 2002:99‐117.
Marks 1992
-
- Marks GB, Dunn SM, Woolcock AJ. A scale for the measurement of quality of life in adults with asthma. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1992;45:461‐72. - PubMed
Meads 2005
-
- Meads C, Nouwen A. Does emotional disclosure have any effects? A systematic review of the literature with meta‐analyses. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2005;21(2):153‐64. - PubMed
Nathan 2004
-
- Nathan RA, Sorkness CA, Kosinski M, Schatz M, Li JT, Marcus P, et al. Development of the asthma control test: a survey for assessing asthma control. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2004;113(1):59‐65. - PubMed
Pennebaker 1986
-
- Pennebaker JW, Beall SK. Confronting a traumatic event: toward an understanding of inhibition and disease. Journal of Abnormal Psychology 1986;95(3):274‐81. - PubMed
Pennebaker 1986a
-
- Pennebaker JW, Hoover C. Inhibition and cognition: toward an understanding of trauma and disease. In: Davidson RJ, Schwartz DW, Shapiro D editor(s). Consciousness and Self Regulation. New York: Plenum, 1986:107‐36.
Pennebaker 1993
-
- Pennebaker JW. Putting stress into words: health, linguistic, and therapeutic implications. Behaviour Research Therapy 1993;31(6):539‐48. - PubMed
RevMan 5 [Computer program]
-
- Copenhagen, The Nordic Cochrane Centre: The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan) Version 5.2. Copenhagen, The Nordic Cochrane Centre: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Smyth 1998
-
- Smyth JM. Written emotional expression: effect sizes, outcome types, and moderating variables. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1998;66(1):174‐84. - PubMed
Wahlgren 1997
-
- Wahlgren DR, Hovell MF, Matt GE, Meltzer SB, Zakarian JM, Meltzer EO. Toward a simplified measure of asthma severity for applied research. Journal of Asthma 1997;34(4):291‐303. - PubMed
Wasserfellan 1997
-
- Wasserfallen JB, Gold K, Schulman KA, Baraniuk JN. Development and validation of a rhinoconjunctivitis and asthma symptom score for use as an outcome measure in clinical trials. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 1997;100(1):16‐22. - PubMed
WHO 2013
-
- WHO. Fact about asthma. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs307/en/ (accessed 6 January 2014).
Wright 1998
Yorke 2005
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

