Genome-wide mapping of IBD segments in an Ashkenazi PD cohort identifies associated haplotypes
- PMID: 24842889
- PMCID: PMC4119402
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddu158
Genome-wide mapping of IBD segments in an Ashkenazi PD cohort identifies associated haplotypes
Abstract
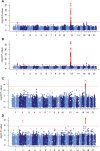
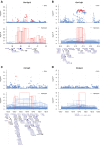
The recent series of large genome-wide association studies in European and Japanese cohorts established that Parkinson disease (PD) has a substantial genetic component. To further investigate the genetic landscape of PD, we performed a genome-wide scan in the largest to date Ashkenazi Jewish cohort of 1130 Parkinson patients and 2611 pooled controls. Motivated by the reduced disease allele heterogeneity and a high degree of identical-by-descent (IBD) haplotype sharing in this founder population, we conducted a haplotype association study based on mapping of shared IBD segments. We observed significant haplotype association signals at three previously implicated Parkinson loci: LRRK2 (OR = 12.05, P = 1.23 × 10(-56)), MAPT (OR = 0.62, P = 1.78 × 10(-11)) and GBA (multiple distinct haplotypes, OR > 8.28, P = 1.13 × 10(-11) and OR = 2.50, P = 1.22 × 10(-9)). In addition, we identified a novel association signal on chr2q14.3 coming from a rare haplotype (OR = 22.58, P = 1.21 × 10(-10)) and replicated it in a secondary cohort of 306 Ashkenazi PD cases and 2583 controls. Our results highlight the power of our haplotype association method, particularly useful in studies of founder populations, and reaffirm the benefits of studying complex diseases in Ashkenazi Jewish cohorts.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Nussbaum R.L., Ellis C.E. Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1356–1364. - PubMed
-
- Do C.B., Tung J.Y., Dorfman E., Kiefer A.K., Drabant E.M., Francke U., Mountain J.L., Goldman S.M., Tanner C.M., Langston J.W., et al. Web-based genome-wide association study identifies two novel loci and a substantial genetic component for Parkinson's disease. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002141. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lesage S., Brice A. Parkinson's disease: from monogenic forms to genetic susceptibility factors. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009;18:R48–R59. - PubMed
-
- Nalls M.A., Plagnol V., Hernandez D.G., Sharma M., Sheerin U.M., Saad M., Simon-Sanchez J., Schulte C., Lesage S., Sveinbjornsdottir S., et al. Imputation of sequence variants for identification of genetic risks for Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet. 2011;377:641–649. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG042188/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS060113/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG021654/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028872/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 NS073836/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2MH089964/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS060113/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089964/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS036630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS050487/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG021654-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS050487/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DK20541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS036630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG028872/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG042188/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG-18728-02A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018728/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

