Genome-wide dynamics of Pol II elongation and its interplay with promoter proximal pausing, chromatin, and exons
- PMID: 24843027
- PMCID: PMC4001325
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.02407
Genome-wide dynamics of Pol II elongation and its interplay with promoter proximal pausing, chromatin, and exons
Abstract
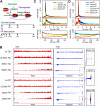
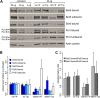
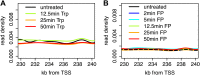
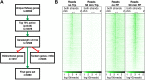
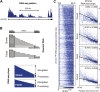
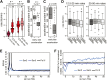
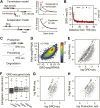
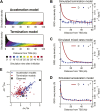
Production of mRNA depends critically on the rate of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) elongation. To dissect Pol II dynamics in mouse ES cells, we inhibited Pol II transcription at either initiation or promoter-proximal pause escape with Triptolide or Flavopiridol, and tracked Pol II kinetically using GRO-seq. Both inhibitors block transcription of more than 95% of genes, showing that pause escape, like initiation, is a ubiquitous and crucial step within the transcription cycle. Moreover, paused Pol II is relatively stable, as evidenced from half-life measurements at ∼3200 genes. Finally, tracking the progression of Pol II after drug treatment establishes Pol II elongation rates at over 1000 genes. Notably, Pol II accelerates dramatically while transcribing through genes, but slows at exons. Furthermore, intergenic variance in elongation rates is substantial, and is influenced by a positive effect of H3K79me2 and negative effects of exon density and CG content within genes.DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02407.001.
Keywords: GRO-seq; P-TEFb; RNA polymerase II; elongation rate; pausing.
Copyright © 2014, Jonkers et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Amit M, Donyo M, Hollander D, Goren A, Kim E, Gelfman S, Lev-Maor G, Burstein D, Schwartz S, Postolsky B, Pupko T, Ast G. 2012. Differential GC content between exons and introns establishes distinct strategies of splice-site recognition. Cell reports 1:543–556. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.03.013 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

