The effects of preemptive tramadol and dexmedetomidine on shivering during arthroscopy
- PMID: 24843340
- PMCID: PMC4024684
- DOI: 10.4103/1658-354X.130729
The effects of preemptive tramadol and dexmedetomidine on shivering during arthroscopy
Abstract
Background: Shivering, the rate of which in regional anesthesia is 39% is an undesired complication seen postoperatively.
Aims: This study aims to compare the ability of preventing the shivering of preemptive tramadol and dexmedetomidine during the spinal anesthesia (SA).
Methods: A total of 90 patients with American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I-II, aged 18-60 years and undergoing elective arthroscopic surgery with SA were divided into three groups randomly. After spinal block, 100 mg tramadol in 100 ml saline was applied in group T- (n = 30) and 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine in 100 ml saline was applied in group D- (n = 30) and 100 ml saline was administered in group P- (n = 30) in 10 min. The hemodynamics, oxygen saturation, tympanic temperature, shivering and sedation scores were evaluated and recorded intraoperatively and 45 min after a postoperative period.
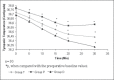
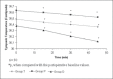
Results: In group T and D, shivering scores were significantly lower when compared with group P in the intraoperative 20(th) min (P = 0.01). Sedation scores in group D were significantly higher than the baseline values (P = 0.03) and values in group T and P (P = 0.04).
Conclusions: Preemptive tramadol and dexmedetomidine are effective in preventing the shivering under SA. In addition, dexmedetomidine was superior in increasing the level of sedation which is sufficient to prevent the anxiety without any adverse effects.
Keywords: Arthroscopic surgery; dexmedetomine; shivering; spinal anesthesia; tramadol.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Buggy DJ, Crossley AW. Thermoregulation, mild perioperative hypothermia and postanesthetic shivering. Br J Anaesth. 2000;84:615–28. - PubMed
-
- Alfonsi P. Postanesthetic shivering: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and approaches to prevention and management. Drugs. 2001;61:2193–205. - PubMed
-
- Chan AM, Ng KF, Tong EW, Jan GS. Control of shivering under regional anesthesia in obstetric patients with tramadol. Canadian journal of anesthesia = Journal canadien d’anesthesie. 1999;46:253–8. - PubMed
-
- Emerick TH, Ozaki M, Sessler DI, Walters K, Schroeder M. Epidural anesthesia increases apparent leg temperature and decreases the shivering threshold. Anesthesiology. 1994;81:289–98. - PubMed
-
- Sessler DI. Complications and treatment of mild hypothermia. Anesthesiology. 2001;95:531–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical