Mild anemia is frequent and associated with micro- and macroangiopathies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 24843443
- PMCID: PMC4014891
- DOI: 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00060.x
Mild anemia is frequent and associated with micro- and macroangiopathies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Aims/Introduction: The present study investigated the frequency of mild anemia, which is not an indication of intensive therapy using drugs, in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and the association of mild anemia with diabetic complications.
Materials and methods: This is a cross-sectional study of 1189 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Anemia was defined as a hemoglobin level <13.5 g/dL in men and <12.0 g/dL in women. The patients with anemia were divided into two groups: (i) grade 1 anemia with a hemoglobin level ≥11.0 g/dL; and (ii) grade 2 anemia with a hemoglobin level <11.0 g/dL.
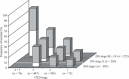
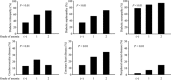
Results: The prevalence of anemia increased with the progression of the stage of diabetic nephropathy and chronic kidney disease. The frequencies of diabetic micro- and macroangiopathies increased with the progression of anemia among 798 patients without anemia, 300 with grade 1 anemia and 91 with grade 2 anemia. Both grade 1 and grade 2 anemia were associated with diabetic micro- and macroangiopathies. They remained independently associated with diabetic retinopathy, coronary heart disease and peripheral arterial disease after adjustment by age, sex, body mass index, use of angiotensin II receptor blocker, estimated glomerular filtration rate and stage of diabetic nephropathy.
Conclusions: Mild anemia is frequent and associated with micro- and macroangiopathies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is important to carry out intensive examinations for the detection of diabetic micro- and macroangiopathies in addition to evaluating the causes of anemia when mild anemia is found in patients with diabetes mellitus. (J Diabetes Invest, doi: 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00060.x, 2010).
Keywords: Anemia; Diabetic nephropathy; eGFR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High frequencies of diabetic micro- and macroangiopathies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate and normoalbuminuria.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010 Apr;25(4):1161-7. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp579. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010. PMID: 19892756
-
Hyperuricemia is independently associated with coronary heart disease and renal dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027817. Epub 2011 Nov 18. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22125626 Free PMC article.
-
The usefulness of the revised classification for chronic kidney disease by the KDIGO for determining the frequency of diabetic micro- and macroangiopathies in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Complications. 2012 Jul-Aug;26(4):286-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2012.04.011. Epub 2012 May 22. J Diabetes Complications. 2012. PMID: 22621778
-
Treatment of diabetic nephropathy with angiotensin II receptor antagonist.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2003 Mar;7(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s101570300000. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 14586737 Review.
-
Approaches to prevention of cardiovascular complications and events in diabetes mellitus.Drugs. 2007;67(7):997-1026. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767070-00005. Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17488145 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between anemia, serum bilirubin concentrations, and diabetic retinopathy in individuals with type 2 diabetes.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Oct;98(43):e17693. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017693. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31651899 Free PMC article.
-
Current Metabolic Status Affects Urinary Liver-Type Fatty-Acid Binding Protein in Normoalbuminuric Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.J Clin Med Res. 2017 Apr;9(4):366-373. doi: 10.14740/jocmr2934w. Epub 2017 Feb 21. J Clin Med Res. 2017. PMID: 28270898 Free PMC article.
-
The Prevalence of the Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis among Type 2 Diabetic Patients Is Greater in the Progressive Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease.Nephron Extra. 2013 Jul 12;3(1):66-72. doi: 10.1159/000353592. Print 2013 Jan. Nephron Extra. 2013. PMID: 23904855 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Baseline Values of Renal Prognosis-related Factors on Their Changes after Initiating Tofogliflozin Treatment: A Retrospective Study in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Renal Impairment.JMA J. 2024 Oct 15;7(4):571-579. doi: 10.31662/jmaj.2024-0128. Epub 2024 Sep 6. JMA J. 2024. PMID: 39513071 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Albumin, but not Bilirubin, is Associated with Diabetic Chronic Vascular Complications in a Chinese Type 2 Diabetic Population.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 19;9(1):12086. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48486-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31427625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomas MC, MacIsaac RJ, Tsalamandris C, et al. Unrecognized anemia in patients with diabetes: a cross‐sectional survey. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 1164–1169 - PubMed
-
- Thomas MC, MacIsaac RJ, Tsalamandris C, et al. Anemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 4359–4363 - PubMed
-
- Al‐Khoury S, Afzali B, Shah N, et al. Anaemia in diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease‐‐prevalence and predictors. Diabetologia 2006; 49: 1183–1189 - PubMed
-
- Wolf G, Müller N, Hunger‐Battefeld W, et al. Hemoglobin concentrations are closely linked to renal function in patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes mellitus. Kidney Blood Press Res 2008; 31: 313–321 - PubMed
-
- New JP, Aung T, Baker PG, et al. The high prevalence of unrecognized anaemia in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a population‐based study. Diabet Med 2008; 25: 564–569 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

