Efficacy of pioglitazone on glycemic control and carotid intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes patients with inadequate insulin therapy
- PMID: 24843462
- PMCID: PMC4008016
- DOI: 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00064.x
Efficacy of pioglitazone on glycemic control and carotid intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes patients with inadequate insulin therapy
Abstract
Aims/Introduction: The present study was designed to determine the effects of pioglitazone on glycemic control and atherosclerosis in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes on insulin therapy.
Materials and methods: The study was a prospective, randomized controlled trial involving 48 patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes treated with insulin. We assigned patients to oral pioglitazone titrated from 15-30 mg (n = 22) or no pioglitazone (n = 26), to be taken in addition to their glucose-lowering drugs and other medications. Daily insulin doses and numbers were recorded during the study period.
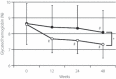
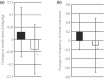
Results: The adjusted mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) values decreased significantly by 1.13 ± 1.50% and 0.55 ± 0.76% in the pioglitazone and control groups, respectively. Significant decrease of HbA1c level was observed in the pioglitazone group compared with the control group (P < 0.05). The insulin dose lowered by 0.04 ± 0.10 units/kg/day in the pioglitazone group and increased by 0.03 ± 0.10 units/kg/day in the control group (P < 0.05). The number of insulin injections decreased by 0.1 ± 0.6 times/day in the pioglitazone group and increased by 0.2 ± 0.4 times/day in the control group (P < 0.05). The carotid intima-media thickness estimated by B-mode echography was carried out in both groups and decreased significantly at the end-point only in the pioglitazone group, relative to the baseline.
Conclusions: These findings show that pioglitazone is useful in improving glycemic control and preventing the progression of atherosclerosis in poorly-controlled type 2 diabetics on insulin therapy. (J Diabetes Invest, doi: 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00064.x, 2010).
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Insulin therapy; Pioglitazone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of replacing metformin with pioglitazone on glycemic control in japanese patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 12-week, open-label, prospective study.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2008 Aug;69(4):364-77. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2008.08.005. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2008. PMID: 24692813 Free PMC article.
-
Pioglitazone decreases carotid intima-media thickness independently of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results from a controlled randomized study.Circulation. 2005 May 17;111(19):2525-31. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000165072.01672.21. Epub 2005 May 9. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 15883215 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of pioglitazone compared with glimepiride on carotid intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial.JAMA. 2006 Dec 6;296(21):2572-81. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.21.joc60158. Epub 2006 Nov 13. JAMA. 2006. PMID: 17101640 Clinical Trial.
-
Sitagliptin added to treatment with ongoing pioglitazone for up to 52 weeks improves glycemic control in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Investig. 2011 Oct 7;2(5):381-90. doi: 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2011.00120.x. J Diabetes Investig. 2011. PMID: 24843518 Free PMC article.
-
Mistakes, misunderstandings and controversies in diabetes: A review and personal account.J Diabetes Investig. 2010 Jun 1;1(3):97-100. doi: 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00012.x. J Diabetes Investig. 2010. PMID: 24843414 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PPAR-Gamma Activation May Inhibit the In Vivo Degeneration of Bioprosthetic Aortic and Aortic Valve Grafts under Diabetic Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 14;22(20):11081. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011081. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681744 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effects of lipid lowering, hypoglycemic, antihypertensive and antiplatelet medications on carotid artery intima-media thickness progression: a network meta-analysis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019 Jan 30;18(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0817-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019. PMID: 30700294 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular effects following intensification of glycemic control in poorly controlled patients with long-standing type 2 diabetes mellitus.Hormones (Athens). 2021 Dec;20(4):783-791. doi: 10.1007/s42000-021-00318-x. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Hormones (Athens). 2021. PMID: 34505233
-
Continuation or discontinuation of pioglitazone when starting bedtime insulin in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes in an inner-city population.J Diabetes Complications. 2015 Nov-Dec;29(8):1248-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.06.013. Epub 2015 Jul 2. J Diabetes Complications. 2015. PMID: 26215435 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term effects of different hypoglycemic drugs on carotid intima-media thickness progression: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 May 31;15:1403606. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1403606. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38883606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The ADVANCE Collaborative Group . Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 2560–2572 - PubMed
-
- Pftzner A, Marx N, Lbben G, et al. Improvement of cardiovascular risk markers by pioglitazone is independent from glycemic control: results from the Pioneer study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005; 45: 1925–1931 - PubMed
-
- Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 129–139 - PubMed
-
- Langenfeld MR, Forst T, Hohberg C, et al. Pioglitazone decreases carotid intima‐media thickness independently of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results from a controlled randomized study. Circulation 2005; 111: 2525–2531 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

