Comparison of spironolactone and trichlormethiazide as add-on therapy to renin-angiotensin blockade for reduction of albuminuria in diabetic patients
- PMID: 24843672
- PMCID: PMC4015670
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12029
Comparison of spironolactone and trichlormethiazide as add-on therapy to renin-angiotensin blockade for reduction of albuminuria in diabetic patients
Abstract
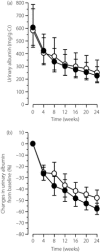
To compare the efficacy of spironolactone and trichlormethiazide, as add-on therapy to renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockade, for reduction of albuminuria in diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we conducted this randomized, open-labeled, parallel-group, active-controlled, per-protocol-design study. Type 2 diabetic patients receiving an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker, with persistent albuminuria (≥100 mg/g creatinine) were randomly assigned to either spironolactone (25 mg/day) or trichlormethiazide (2 mg/day). The primary outcome was the change in albuminuria at 24 weeks of treatment. In patients who completed 24 weeks of treatment with spironolactone (n = 18) and trichlormethiazide (n = 15), albuminuria decreased significantly by -57.6 ± 21.3% (SD) (P < 0.001) and -48.4 ± 27.1% (P < 0.001), respectively. There was no significant difference in the change in albuminuria between groups (P = 0.270). This pilot study suggests add-on therapy with spironolactone or trichlormethiazide to RAS blockade may be comparably beneficial to reducing albuminuria in type 2 diabetic patients. This trial was registered with UMIN-CTR (no. UMIN000008914).
Keywords: Aldosterone blockers; Diabetic kidney disease; Thiazide diuretics.
Figures
References
-
- Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, et al The effect of angiotensin‐converting‐enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The collaborative study group. N Engl J Med 1993; 329: 1456–1462 - PubMed
-
- Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, et al Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 861–869 - PubMed
-
- Epstein M. Aldosterone and the hypertensive kidney: its emerging role as a mediator of progressive renal dysfunction; a paradigm shift. J Hypertens 2001; 19: 829–842 - PubMed
-
- Chrysostomou A, Becker G. Spironolactone in addition to ACE Inhibition to reduce proteinuria in patients with chronic renal disease. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 925–926 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

