Uptake of Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli SubAB by HeLa cells requires an actin- and lipid raft-dependent pathway
- PMID: 24844382
- PMCID: PMC4241268
- DOI: 10.1111/cmi.12315
Uptake of Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli SubAB by HeLa cells requires an actin- and lipid raft-dependent pathway
Abstract
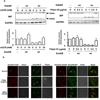
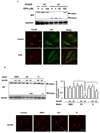
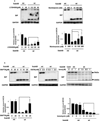
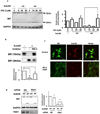
The novel cytotoxic factor subtilase cytotoxin (SubAB) is produced mainly by non-O157 Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli (STEC). SubAB cleaves the molecular chaperone BiP/GRP78 in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), leading to activation of RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR)-like ER kinase (PERK), followed by caspase-dependent cell death. However, the SubAB uptake mechanism in HeLa cells is unknown. In this study, a variety of inhibitors and siRNAs were employed to characterize the SubAB uptake process. SubAB-induced BiP cleavage was inhibited by high concentrations of Dynasore, and methyl-β-cyclodextrin (mβCD) and Filipin III, but not suppressed in clathrin-, dynamin I/II-, caveolin1- and caveolin2-knockdown cells. We observed that SubAB treatment led to dramatic actin rearrangements, e.g. formation of plasma membrane blebs, with a significant increase in fluid uptake. Confocal microscopy analysis showed that SubAB uptake required actin cytoskeleton remodelling and lipid raft cholesterol. Furthermore, internalized SubAB in cells was found in the detergent-resistant domain (DRM) structure. Interestingly, IPA-3, an inhibitor of serine/threonine kinase p21-activated kinase (PAK1), an important protein of macropinocytosis, directly inhibited SubAB-mediated BiP cleavage and SubAB internalization. Thus, our findings suggest that SubAB uses lipid raft- and actin-dependent, but not clathrin-, caveolin- and dynamin-dependent pathways as its major endocytic translocation route.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Subtilase cytotoxin produced by locus of enterocyte effacement-negative Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli induces stress granule formation.Cell Microbiol. 2016 Jul;18(7):1024-40. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12565. Epub 2016 Feb 21. Cell Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26749168 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of subtilase cytotoxin-induced cell death by an RNA-dependent protein kinase-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase-dependent proteasome pathway in HeLa cells.Infect Immun. 2012 May;80(5):1803-14. doi: 10.1128/IAI.06164-11. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22354021 Free PMC article.
-
Host response to the subtilase cytotoxin produced by locus of enterocyte effacement-negative Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli.Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Oct;64(10):657-665. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12841. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32902863 Review.
-
Clathrin-dependent trafficking of subtilase cytotoxin, a novel AB5 toxin that targets the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP.Cell Microbiol. 2008 Mar;10(3):795-806. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01085.x. Epub 2007 Nov 27. Cell Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18042253
-
A dietary non-human sialic acid may facilitate hemolytic-uremic syndrome.Kidney Int. 2009 Jul;76(2):140-4. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.131. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Kidney Int. 2009. PMID: 19387473 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Subtilase cytotoxin induces a novel form of Lipocalin 2, which promotes Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli survival.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 3;10(1):18943. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76027-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33144618 Free PMC article.
-
Subtilase cytotoxin produced by locus of enterocyte effacement-negative Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli induces stress granule formation.Cell Microbiol. 2016 Jul;18(7):1024-40. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12565. Epub 2016 Feb 21. Cell Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26749168 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Membrane Vesicles: Physiological Roles, Infection Immunology, and Applications.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Sep;10(25):e2301357. doi: 10.1002/advs.202301357. Epub 2023 Jun 25. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37357142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compounds with anti-influenza activity: present and future of strategies for the optimal treatment and management of influenza. Part I: Influenza life-cycle and currently available drugs.J Prev Med Hyg. 2014 Sep;55(3):69-85. J Prev Med Hyg. 2014. PMID: 25902573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) as a therapeutic target for cardiotoxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2022 Dec;96(12):3143-3162. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03384-1. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36116095 Review.
References
-
- Boquet P, Ricci V. Intoxication strategy of Helicobacter pylori VacA toxin. Trends Microbiol. 2012;20:165–174. - PubMed
-
- Chong DC, Paton JC, Thorpe CM, Paton AW. Clathrin-dependent trafficking of subtilase cytotoxin, a novel AB5 toxin that targets the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP. Cell Microbiol. 2008;10:795–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

