Comparison of estimates of left ventricular ejection fraction obtained from gated blood pool imaging, different software packages and cameras
- PMID: 24844547
- PMCID: PMC4026769
- DOI: 10.5830/CVJA-2013-082
Comparison of estimates of left ventricular ejection fraction obtained from gated blood pool imaging, different software packages and cameras
Abstract
Objective: To determine how two software packages, supplied by Siemens and Hermes, for processing gated blood pool (GBP) studies should be used in our department and whether the use of different cameras for the acquisition of raw data influences the results.
Methods: The study had two components. For the first component, 200 studies were acquired on a General Electric (GE) camera and processed three times by three operators using the Siemens and Hermes software packages. For the second part, 200 studies were acquired on two different cameras (GE and Siemens). The matched pairs of raw data were processed by one operator using the Siemens and Hermes software packages.
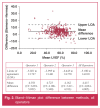
Results: The Siemens method consistently gave estimates that were 4.3% higher than the Hermes method (p < 0.001). The differences were not associated with any particular level of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). There was no difference in the estimates of LVEF obtained by the three operators (p = 0.1794). The reproducibility of estimates was good. In 95% of patients, using the Siemens method, the SD of the three estimates of LVEF by operator 1 was ≤ 1.7, operator 2 was ≤ 2.1 and operator 3 was ≤ 1.3. The corresponding values for the Hermes method were ≤ 2.5, ≤ 2.0 and ≤ 2.1. There was no difference in the results of matched pairs of data acquired on different cameras (p = 0.4933) CONCLUSION: Software packages for processing GBP studies are not interchangeable. The report should include the name and version of the software package used. Wherever possible, the same package should be used for serial studies. If this is not possible, the report should include the limits of agreement of the different packages. Data acquisition on different cameras did not influence the results.
Figures
References
-
- Hesse B, Lindhardt TB, Acampa W, Anagnostopoulos C, Ballinger J, Bax JJ. et al. EANM/ESC guidelines for radionuclide imaging of cardiac function. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35(4):851–885. - PubMed
-
- Hendel RC, Berman DS, Di Carli MF, Heidenreich PA, Henkin RE, Pellikka PA. ACCF/ASNC/ACR/AHA/ASE/SCCT/SCMR/SNM 2009 appropriate use criteria for cardiac radionuclide imaging: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology, the American College of Radiology, the American Heart Association, the American Society of Echocardiography, the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, and the Society of Nuclear Medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(23):2201–2229. - PubMed
-
- Hiscock SC, Evans MJ, Morton RJ, Hall DO. Investigation of normal ranges for left ventricular ejection fraction in cardiac gated blood pool imaging studies using different processing workstations. Nucl Med Commun. 2008;29(2):103–109. - PubMed
-
- Skrypniuk JV, Bailey D, Cosgriff PS, Fleming JS, Houston AS, Jarritt PH. et al. UK audit of left ventricular ejection fraction estimation from equilibrium ECG gated blood pool images. Nucl Med Commun. 2005;26(3):205–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials