Targeting the disordered C terminus of PTP1B with an allosteric inhibitor
- PMID: 24845231
- PMCID: PMC4062594
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1528
Targeting the disordered C terminus of PTP1B with an allosteric inhibitor
Abstract
PTP1B, a validated therapeutic target for diabetes and obesity, has a critical positive role in HER2 signaling in breast tumorigenesis. Efforts to develop therapeutic inhibitors of PTP1B have been frustrated by the chemical properties of the active site. We define a new mechanism of allosteric inhibition that targets the C-terminal, noncatalytic segment of PTP1B. We present what is to our knowledge the first ensemble structure of PTP1B containing this intrinsically disordered segment, within which we identified a binding site for the small-molecule inhibitor MSI-1436. We demonstrate binding to a second site close to the catalytic domain, with cooperative effects between the two sites locking PTP1B in an inactive state. MSI-1436 antagonized HER2 signaling, inhibited tumorigenesis in xenografts and abrogated metastasis in the NDL2 mouse model of breast cancer, validating inhibition of PTP1B as a therapeutic strategy in breast cancer. This new approach to inhibition of PTP1B emphasizes the potential of disordered segments of proteins as specific binding sites for therapeutic small molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
A company called DepYmed Inc was founded on 3 March 2014 with the primary purpose of taking MSI-1436 into the clinic in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. It is owned 50-50 by Ohr Pharmaceuticals and Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Authors Krishnan and Tonks would be entitled to a share based upon the conditions of the Invention Agreement signed by all scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Lab.
Figures
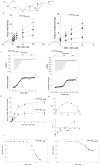

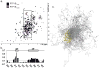

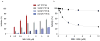

References
-
- Slamon DJ, et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989;244:707–12. - PubMed
-
- Tiwari RK, Borgen PI, Wong GY, Cordon-Cardo C, Osborne MP. HER-2/neu amplification and overexpression in primary human breast cancer is associated with early metastasis. Anticancer Research. 1992;12:419–25. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Settleman J. Acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors during cancer therapy. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 2008;18:73–9. - PubMed
-
- Tonks NK, Diltz CD, Fischer EH. Purification of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1988;263:6722–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM100910/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM098482/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM098482/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM55989/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA45508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA53840/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA053840/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM100910/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA053840/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR017269/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM055989/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA045508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10-RR017269/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

