Noninvasive imaging of the high frequency brain activity in focal epilepsy patients
- PMID: 24845275
- PMCID: PMC4123538
- DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2013.2297332
Noninvasive imaging of the high frequency brain activity in focal epilepsy patients
Erratum in
-
Corrections to "Noninvasive Imaging of the High Frequency Brain Activity in Focal Epilepsy Patients".IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015 Aug;62(8):2092. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2015.2450531. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015. PMID: 26186751 No abstract available.
Abstract
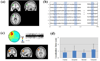
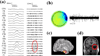
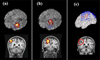
High-frequency (HF) activity represents a potential biomarker of the epileptogenic zone in epilepsy patients, the removal of which is considered to be crucial for seizure-free surgical outcome. We proposed a high frequency source imaging (HFSI) approach to noninvasively image the brain sources of the scalp-recorded HF EEG activity. Both computer simulation and clinical patient data analysis were performed to investigate the feasibility of using the HFSI approach to image the sources of HF activity from noninvasive scalp EEG recordings. The HF activity was identified from high-density scalp recordings after high-pass filtering the EEG data and the EEG segments with HF activity were concatenated together to form repetitive HF activity. Independent component analysis was utilized to extract the components corresponding to the HF activity. Noninvasive EEG source imaging using realistic geometric boundary element head modeling was then applied to image the sources of the pathological HF brain activity. Five medically intractable focal epilepsy patients were studied and the estimated sources were found to be concordant with the surgical resection or intracranial recordings of the patients. The present study demonstrates, for the first time, that source imaging from the scalp HF activity could help to localize the seizure onset zone and provide a novel noninvasive way of studying the epileptic brain in humans. This study also indicates the potential application of studying HF activity in the presurgical planning of medically intractable epilepsy patients.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Noninvasive cortical imaging of epileptiform activities from interictal spikes in pediatric patients.Neuroimage. 2011 Jan 1;54(1):244-52. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.07.026. Epub 2010 Jul 17. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 20643212 Free PMC article.
-
Seizure source imaging by means of FINE spatio-temporal dipole localization and directed transfer function in partial epilepsy patients.Clin Neurophysiol. 2012 Jul;123(7):1275-83. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2011.11.007. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Clin Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22172768 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Ictal Source Imaging for Localizing Seizure Onset Zone in Patients With Focal Epilepsy.Neurology. 2021 Jan 19;96(3):e366-e375. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000011109. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Neurology. 2021. PMID: 33097598 Free PMC article.
-
From theory to practical fundamentals of electroencephalographic source imaging in localizing the epileptogenic zone.Epilepsia. 2022 Oct;63(10):2476-2490. doi: 10.1111/epi.17361. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Epilepsia. 2022. PMID: 35811476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous EEG and fMRI recordings (EEG-fMRI) in children with epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2013 Jun;54(6):971-82. doi: 10.1111/epi.12197. Epub 2013 May 3. Epilepsia. 2013. PMID: 23647021 Review.
Cited by
-
Resting-state test-retest reliability of a priori defined canonical networks over different preprocessing steps.Brain Struct Funct. 2017 Apr;222(3):1447-1468. doi: 10.1007/s00429-016-1286-x. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. PMID: 27550015 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetoencephalography imaging of high frequency oscillations strengthens presurgical localization and outcome prediction.Brain. 2019 Nov 1;142(11):3514-3529. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz284. Brain. 2019. PMID: 31553044 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of functional brain activity and connectivity using EEG and fMRI in patients with sickle cell disease.Neuroimage Clin. 2016 Dec 26;14:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.12.024. eCollection 2017. Neuroimage Clin. 2016. PMID: 28116239 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Programming and Frequent Itemset Mining to Identify Feature Selection Patterns of iEEG and fMRI Epilepsy Data.Eng Appl Artif Intell. 2015 Mar;39:198-214. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2014.12.008. Eng Appl Artif Intell. 2015. PMID: 25580059 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive Electromagnetic Source Imaging and Granger Causality Analysis: An Electrophysiological Connectome (eConnectome) Approach.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2016 Dec;63(12):2474-2487. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2016.2616474. Epub 2016 Oct 11. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2016. PMID: 27740473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cascino GD. Commentary: how has neuroimaging improved patient care? Epilepsia. 1994;35(6):S103–S107. - PubMed
-
- Morrell MJ. Responsive cortical stimulation for the treatment of medically intractable partial epilepsy. Neurology. 2011;77(13):1295–1304. - PubMed
-
- Engel J., Jr. Approaches to localization of the epileptogenic lesion. In: Engel J Jr., editor. Surgical Treatment of the Epilepsies. New York: Raven Press; 1987. pp. 75–95.
-
- Rosenow F, Lüders H. Presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Brain. 2001;124(9):1683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

