Materials as stem cell regulators
- PMID: 24845994
- PMCID: PMC4163547
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat3937
Materials as stem cell regulators
Erratum in
- Nat Mater. 2014 Jul;13(7):756
Abstract
The stem cell/material interface is a complex, dynamic microenvironment in which the cell and the material cooperatively dictate one another's fate: the cell by remodelling its surroundings, and the material through its inherent properties (such as adhesivity, stiffness, nanostructure or degradability). Stem cells in contact with materials are able to sense their properties, integrate cues via signal propagation and ultimately translate parallel signalling information into cell fate decisions. However, discovering the mechanisms by which stem cells respond to inherent material characteristics is challenging because of the highly complex, multicomponent signalling milieu present in the stem cell environment. In this Review, we discuss recent evidence that shows that inherent material properties may be engineered to dictate stem cell fate decisions, and overview a subset of the operative signal transduction mechanisms that have begun to emerge. Further developments in stem cell engineering and mechanotransduction are poised to have substantial implications for stem cell biology and regenerative medicine.
Figures

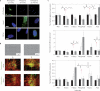

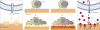
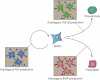

References
-
- Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126:677–689. - PubMed
-
- Lee J, Abdeen AA, Zhang D, Kilian KA. Directing stem cell fate on hydrogel substrates by controlling cell geometry, matrix mechanics and adhesion ligand composition. Biomaterials. 2013;34:8140–8148. - PubMed
-
- Dalby MJ, et al. The control of human mesenchymal cell differentiation using nanoscale symmetry and disorder. Nature Mater. 2007;6:997–1003. - PubMed
-
- McMurray RJ, et al. Nanoscale surfaces for the long-term maintenance of mesenchymal stem cell phenotype and multipotency. Nature Mater. 2011;10:637–644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

