Serum amyloid A induces NLRP-3-mediated IL-1β secretion in neutrophils
- PMID: 24846290
- PMCID: PMC4028190
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096703
Serum amyloid A induces NLRP-3-mediated IL-1β secretion in neutrophils
Abstract
Background/aims: Serum amyloid A (SAA) is an acute phase reactant with significant immunological activities, including effects on cytokine synthesis and neutrophil chemotaxis. Neutrophils can also release cytokines with proinflammatory properties. IL-1β is a key proinflammatory cytokine, the secretion of which is controlled by inflammasome. We investigated the proinflammatory effects of SAA in vitro in relation to the NLRP3 inflammasome in neutrophils.
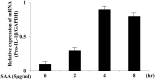
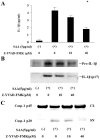
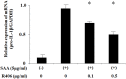
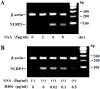
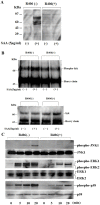
Methodology/principal findings: Human neutrophils isolated form healthy subjects were stimulated with serum amyloid A (SAA). The cellular supernatants were analyzed by western blot using anti-IL-1β or anti-caspase-1 antibodies. IL-1β or Nod-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) mRNA expressions were analyzed by real-time PCR or reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) method. SAA stimulation induced pro-IL-1β mRNA expression in neutrophils. Furthermore, SAA engaged the caspase-1-activating inflammasome, resulting in the production of active IL-1β. SAA-induced pro-IL-1β expression was marginally suppressed by the Syk specific inhibitor, R406, and SAA-induced pro-IL-1β processing in neutrophils was prevented by R406. Furthermore, SAA-induced NLRP3 mRNA expression was completely blocked by R406. Analysis of intracellular signaling revealed that SAA stimulation activated the tyrosine kinase Syk and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK).
Conclusions/significance: These results demonstrate that the innate neutrophil immune response against SAA involves a two-step activation process: an initial signal promoting expression of pro-IL-1β and a second signal involving Syk-dependent activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and caspase-1, allowing processing of pro-IL-1β and secretion of mature IL-1β.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Uhlar CM, Whitehead AS (1999) Serum amyloid A, the major vertebrate acute-phase reactant. Eur J Biochem 265: 501–23. - PubMed
-
- Cunnane G, Whitehead AS (1999) Amyloid precursors and amyloidosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 13: 615–28. - PubMed
-
- Eklund KK, Niemi K, Kovanen PT (2012) Immune functions of serum amyloid A. Crit Rev Immunol. 32: 335–48. - PubMed
-
- Niemi K, Teirilä L, Lappalainen J, Rajamäki K, Baumann MH, et al. (2011) Serum amyloid A activates the NLRP3 inflammasome via P2×7 receptor and a cathepsin B-sensitive pathway. J Immunol 186: 6119–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

