Highly accelerated aortic 4D flow MR imaging with variable-density random undersampling
- PMID: 24846341
- PMCID: PMC4135010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2014.05.004
Highly accelerated aortic 4D flow MR imaging with variable-density random undersampling
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate an effective time-resolved variable-density random undersampling scheme combined with an efficient parallel image reconstruction method for highly accelerated aortic 4D flow MR imaging with high reconstruction accuracy.
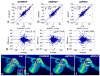
Materials and methods: Variable-density Poisson-disk sampling (vPDS) was applied in both the phase-slice encoding plane and the temporal domain to accelerate the time-resolved 3D Cartesian acquisition of flow imaging. In order to generate an improved initial solution for the iterative self-consistent parallel imaging method (SPIRiT), a sample-selective view sharing reconstruction for time-resolved random undersampling (STIRRUP) was introduced. The performance of different undersampling and image reconstruction schemes were evaluated by retrospectively applying those to fully sampled data sets obtained from three healthy subjects and a flow phantom.
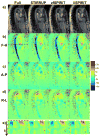
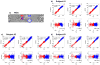
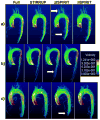
Results: Undersampling pattern based on the combination of time-resolved vPDS, the temporal sharing scheme STIRRUP, and parallel imaging SPIRiT, were able to achieve 6-fold accelerated 4D flow MRI with high accuracy using a small number of coils (N=5). The normalized root mean square error between aorta flow waveforms obtained with the acceleration method and the fully sampled data in three healthy subjects was 0.04±0.02, and the difference in peak-systolic mean velocity was -0.29±2.56cm/s.
Conclusion: Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of our preliminary results demonstrate that time-resolved variable-density random sampling is efficient for highly accelerating 4D flow imaging while maintaining image reconstruction accuracy.
Keywords: Flow; Parallel imaging; Random; Time-resolved; Undersampling; View sharing.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
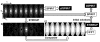



References
-
- Pruessmann KP, et al. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magnetic resonance in medicine: official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine/Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1999;42(5):952–62. - PubMed
-
- Griswold MA, et al. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA) Magnetic resonance in medicine: official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine/Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2002;47(6):1202–10. - PubMed
-
- Beerbaum P, et al. Rapid left-to-right shunt quantification in children by phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging combined with sensitivity encoding (SENSE) Circulation. 2003;108(11):1355–61. - PubMed
-
- Baltes C, et al. Accelerating cine phase-contrast flow measurements using k-t BLAST and k-t SENSE. Magnetic resonance in medicine: official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine/Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2005;54(6):1430–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

