NK cell-extrinsic IL-18 signaling is required for efficient NK-cell activation by vaccinia virus
- PMID: 24846540
- PMCID: PMC4165707
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201344134
NK cell-extrinsic IL-18 signaling is required for efficient NK-cell activation by vaccinia virus
Abstract
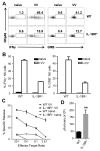
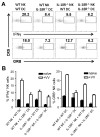
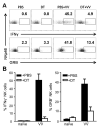
NK cells are important for the control of vaccinia virus (VV) in vivo. Recent studies have shown that multiple pathways are required for effective activation of NK cells. These include both TLR-dependent and -independent pathways, as well as the NKG2D activating receptor that recognizes host stress-induced NKG2D ligands. However, it remains largely unknown what controls the upregulation of NKG2D ligands in response to VV infection. In this study using C57BL/6 mice, we first showed that IL-18 is critical for NK-cell activation and viral clearance. We then demonstrated that IL-18 signaling on both NK cells and DCs is required for efficient NK-cell activation upon VV infection in vitro. We further showed in vivo that efficient NK-cell activation in response to VV is dependent on DCs and IL-18 signaling in non-NK cells, suggesting an essential role for NK cell-extrinsic IL-18 signaling in NK-cell activation. Mechanistically, IL-18 signaling in DCs promotes expression of Rae-1, an NKG2D ligand. Collectively, our data reveal a previously unrecognized role for NK cell-extrinsic IL-18 signaling in NK-cell activation through upregulation of NKG2D ligands. These observations may provide insights into the design of effective NK-cell-based therapies for viral infections and cancer.
Keywords: IL-18; NK cells; NKG2D; Rae-1; Vaccinia virus.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
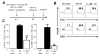
References
-
- Lee SH, Miyagi T, Biron CA. Keeping NK cells in highly regulated antiviral warfare. Trends Immunol. 2007;28:252–259. - PubMed
-
- Bukowski JF, Woda BA, Habu S, Okumura K, Welsh RM. Natural killer cell depletion enhances virus synthesis and virus-induced hepatitis in vivo. J Immunol. 1983;131:1531–1538. - PubMed
-
- Natuk RJ, Welsh RM. Accumulation and chemotaxis of natural killer/large granular lymphocytes at sites of virus replication. J Immunol. 1987;138:877–883. - PubMed
-
- Martinez J, Huang X, Yang Y. Direct action of type I IFN on NK cells is required for their activation in response to vaccinia viral infection in vivo. J Immunol. 2008;180:1592–1597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

