Orexin A activates hypoglossal motoneurons and enhances genioglossus muscle activity in rats
- PMID: 24846570
- PMCID: PMC4241090
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12784
Orexin A activates hypoglossal motoneurons and enhances genioglossus muscle activity in rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Orexins have been demonstrated to play important roles in many physiological processes. However, it is not known how orexin A affects the activity of the hypoglossal motoneuron (HMN) and genioglossus (GG) muscle.
Experimental approach: GG muscle electromyograms (GG-EMG) were recorded in anaesthetized adult rats after orexin A or orexin receptor antagonists were applied to the hypoglossal nucleus, and in adult rats in which orexin neurons were lesioned with the neurotoxin orexin-saporin (orexin-SAP). HMN membrane potential and firing were recorded from neonatal rat brain slices using whole-cell patch clamp after an infusion of orexin A or orexin receptor antagonists.
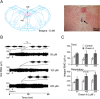
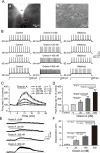
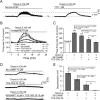
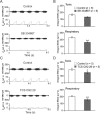
Key results: Unilateral micro-injection of orexin A (50, 100 or 200 μM) into the hypoglossal nucleus significantly enhanced ipsilateral GG activity in adult rats. Orexin A (4, 20, 100 or 500 nM) depolarized the resting membrane potential and increased the firing rate of HMNs in a dose-dependent manner in the medullary slices of neonatal rats. Both SB 334867, a specific OX1 receptor antagonist and TCS OX2 29, a specific OX2 receptor antagonist not only blocked the depolarized membrane potential and the increased firing rate of HMNs by orexin A in the neonatal model but also attenuated GG-EMG in the adult model. A significant decrease in GG-EMG was observed in adult orexin neuron-lesioned rats compared with sham animals.
Conclusion and implications: Orexin A activates OX1 and OX2 receptors within the hypoglossal motor pool and promotes GG activity, indicating that orexin A is involved in controlling respiratory motor activity.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Azhdari-Zarmehri H, Esmaeili MH, Sofiabadi M, Haghdoost-Yazdi H. Orexin receptor type-1 antagonist SB-334867 decreases morphine-induced antinociceptive effect in formalin test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013;112:64–70. - PubMed
-
- Berger AJ, Bayliss DA, Viana F. Development of hypoglossal motoneurons. J Appl Physiol. 1996;81:1039–1048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

