The cytotoxicity of (-)-lomaiviticin A arises from induction of double-strand breaks in DNA
- PMID: 24848236
- PMCID: PMC4090708
- DOI: 10.1038/nchem.1944
The cytotoxicity of (-)-lomaiviticin A arises from induction of double-strand breaks in DNA
Abstract
The metabolite (-)-lomaiviticin A, which contains two diazotetrahydrobenzo[b]fluorene (diazofluorene) functional groups, inhibits the growth of cultured human cancer cells at nanomolar-picomolar concentrations; however, the mechanism responsible for the potent cytotoxicity of this natural product is not known. Here we report that (-)-lomaiviticin A nicks and cleaves plasmid DNA by a pathway that is independent of reactive oxygen species and iron, and that the potent cytotoxicity of (-)-lomaiviticin A arises from the induction of DNA double-strand breaks (dsbs). In a plasmid cleavage assay, the ratio of single-strand breaks (ssbs) to dsbs is 5.3 ± 0.6:1. Labelling studies suggest that this cleavage occurs via a radical pathway. The structurally related isolates (-)-lomaiviticin C and (-)-kinamycin C, which contain one diazofluorene, are demonstrated to be much less effective DNA cleavage agents, thereby providing an explanation for the enhanced cytotoxicity of (-)-lomaiviticin A compared to that of other members of this family.
Figures
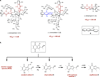
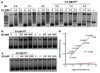





Comment in
-
Natural products: DNA double whammy.Nat Chem. 2014 Jun;6(6):464-5. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1965. Nat Chem. 2014. PMID: 24848229 No abstract available.
References
-
- He H, et al. Lomaiviticins A and B, Potent Antitumor Antibiotics from Micromonospora lomaivitiensis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:5362–5363. - PubMed
-
- Woo CM, Beizer NE, Janso JE, Herzon SB. Isolation of Lomaiviticins C–E. Transformation of Lomaiviticin C to Lomaiviticin A, Complete Structure Elucidation of Lomaiviticin A, and Structure–Activity Analyses. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:15285–15288. - PubMed
-
- Ito S, Matsuya T, Ōmura S, Otani M, Nakagawa A. A New Antibiotic, Kinamycin. J. Antibiot. 1970;23:315–317. - PubMed
-
- Hata T, Ōmura S, Iwai Y, Nakagawa A, Otani M. A New Antibiotic, Kinamycin: Fermentation, Isolation, Purification and Properties. J. Antibiot. 1971;24:353–359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

