Rapid renal alpha-1 antitrypsin gene induction in experimental and clinical acute kidney injury
- PMID: 24848503
- PMCID: PMC4029978
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098380
Rapid renal alpha-1 antitrypsin gene induction in experimental and clinical acute kidney injury
Abstract
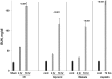
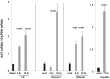
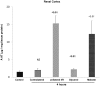
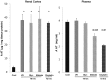
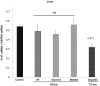
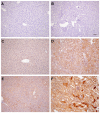
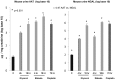
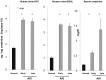
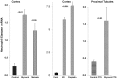
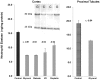
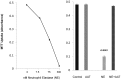
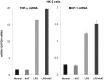
Alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT) is a hepatic stress protein with protease inhibitor activity. Recent evidence indicates that ischemic or toxic injury can evoke selective changes within kidney that resemble a hepatic phenotype. Hence, we tested the following: i) Does acute kidney injury (AKI) up-regulate the normally renal silent AAT gene? ii) Does rapid urinary AAT excretion result? And iii) Can AAT's anti-protease/anti-neutrophil elastase (NE) activity protect injured proximal tubule cells? CD-1 mice were subjected to ischemic or nephrotoxic (glycerol, maleate, cisplatin) AKI. Renal functional and biochemical assessments were made 4-72 hrs later. Rapidly following injury, 5-10 fold renal cortical and isolated proximal tubule AAT mRNA and protein increases occurred. These were paralleled by rapid (>100 fold) increases in urinary AAT excretion. AKI also induced marked increases in renal cortical/isolated proximal tubule NE mRNA. However, sharp NE protein levels declines resulted, which strikingly correlated (r, -0.94) with rising AAT protein levels (reflecting NE complexing by AAT/destruction). NE addition to HK-2 cells evoked ∼95% cell death. AAT completely blocked this NE toxicity, as well as Fe induced oxidant HK-2 cell attack. Translational relevance of experimental AAT gene induction was indicated by ∼100-1000 fold urinary AAT increases in 22 AKI patients (matching urine NGAL increases). We conclude: i) AKI rapidly up-regulates the renal cortical/proximal tubule AAT gene; ii) NE gene induction also results; iii) AAT can confer cytoprotection, potentially by blocking/reducing cytotoxic NE accumulation; and iv) marked increases in urinary AAT excretion in AKI patients implies clinical relevance of the AKI- AAT induction pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proximal tubule haptoglobin gene activation is an integral component of the acute kidney injury "stress response".Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Jul 1;303(1):F139-48. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00168.2012. Epub 2012 May 9. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22573378 Free PMC article.
-
Renal cortical albumin gene induction and urinary albumin excretion in response to acute kidney injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Mar;300(3):F628-38. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00654.2010. Epub 2010 Dec 8. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21147844 Free PMC article.
-
Renal cortical hemopexin accumulation in response to acute kidney injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Nov 15;303(10):F1460-72. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00426.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22993068 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency: Genetic variations, clinical manifestations and therapeutic interventions.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2017 Jul;773:14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 18. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2017. PMID: 28927525 Review.
-
The lipid ties of α1-antitrypsin: Structural and functional aspects.Cell Immunol. 2022 May;375:104528. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2022.104528. Epub 2022 Apr 16. Cell Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35468329 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances of Proteomics in Management of Acute Kidney Injury.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;13(16):2648. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13162648. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative differential proteomic analysis of minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Feb 3;18(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0452-6. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28158993 Free PMC article.
-
Combined iron sucrose and protoporphyrin treatment protects against ischemic and toxin-mediated acute renal failure.Kidney Int. 2016 Jul;90(1):67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.01.022. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 27165818 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of SERPINA3 as a candidate urinary biomarker of lupus nephritis activity.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Feb 1;58(2):321-330. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key301. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 30285245 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of Purified Alpha-1 Antitrypsin in Salt-Loaded Hypertensive 129Sv Mice Attenuates the Expression of Inflammatory Associated Proteins in the Kidney.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 30;15(7):951. doi: 10.3390/biom15070951. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McCullough PA, Shaw AD, Haase M, Bouchard J, Waikar SS, et al. (2013) Diagnosis of acute kidney injury using functional and injury biomarkers: workgroup statements from the tenth Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Consensus Conference. Contrib Nephrol 182: 13–29. - PubMed
-
- Makris K, Rizos D, Kafkas N, Haliassos A (2012) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a new biomarker in laboratory medicine. Clin Chem Lab Med 50: 1519–1532. - PubMed
-
- Bonventre JV, Yang L (2010) Kidney injury molecule-1. Curr Opin Crit Care 16: 556–561. - PubMed
-
- Bonventre JV (2008) Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): a specific and sensitive biomarker of kidney injury. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl 241: 78–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

