1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 reduces cerebral amyloid-β accumulation and improves cognition in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 24849345
- PMCID: PMC6608194
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2711-13.2014
1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 reduces cerebral amyloid-β accumulation and improves cognition in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
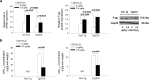
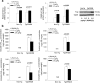
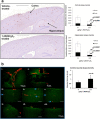
We demonstrate a role of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) in reducing cerebral soluble and insoluble amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides. Short-term treatment of two human amyloid precursor protein-expressing models, Tg2576 and TgCRND8 mice, with 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D3], the endogenous active ligand of VDR, resulted in higher brain P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and lower soluble Aβ levels, effects negated with coadministration of elacridar, a P-gp inhibitor. Long-term treatment of TgCRND8 mice with 1,25(OH)2D3 during the period of plaque formation reduced soluble and insoluble plaque-associated Aβ, particularly in the hippocampus in which the VDR is abundant and P-gp induction is greatest after 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment, and this led to improved conditioned fear memory. In mice fed a vitamin D-deficient diet, lower cerebral P-gp expression was observed, but levels were restored on replenishment with VDR ligands. The composite data suggest that the VDR is an important therapeutic target in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer's; P-glycoprotein; amyloid beta; blood-brain barrier; vitamin D receptor.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/347091-11$15.00/0.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Lack of P-glycoprotein Results in Impairment of Removal of Beta-Amyloid and Increased Intraparenchymal Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy after Active Immunization in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2017;14(6):656-667. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666161201201227. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2017. PMID: 27915995
-
Berberine ameliorates β-amyloid pathology, gliosis, and cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer's disease transgenic mouse model.Neurobiol Aging. 2012 Dec;33(12):2903-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.02.016. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Neurobiol Aging. 2012. PMID: 22459600
-
Human Alzheimer's disease gene expression signatures and immune profile in APP mouse models: a discrete transcriptomic view of Aβ plaque pathology.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Sep 6;15(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1265-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30189875 Free PMC article.
-
L-3-n-butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment and reduces amyloid-beta in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci. 2010 Jun 16;30(24):8180-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0340-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20554868 Free PMC article.
-
Neutral Sphingomyelinase-2 Deficiency Ameliorates Alzheimer's Disease Pathology and Improves Cognition in the 5XFAD Mouse.J Neurosci. 2016 Aug 17;36(33):8653-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1429-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27535912 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Induction of P-Glycoprotein Function can be Measured with [18F]MC225 and PET.Mol Pharm. 2021 Aug 2;18(8):3073-3085. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00302. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Mol Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34228458 Free PMC article.
-
1,25-Dihydroxy Vitamin D3 Facilitates the M2 Polarization and β-Amyloid Uptake by Human Microglia in a TREM2-Dependent Manner.Biomed Res Int. 2023 May 27;2023:3483411. doi: 10.1155/2023/3483411. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37274074 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Reduced Folate Carrier (RFC) by Vitamin D Receptor at the Blood-Brain Barrier.Mol Pharm. 2017 Nov 6;14(11):3848-3858. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00572. Epub 2017 Sep 26. Mol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28885847 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D supplementation has no effects on progression of motor dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020 Jan;74(1):167-175. doi: 10.1038/s41430-019-0448-3. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31197218 Clinical Trial.
-
Serum Parathyroid Hormone, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, and Risk of Alzheimer's Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study.Nutrients. 2018 Sep 6;10(9):1243. doi: 10.3390/nu10091243. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30200567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bauer B, Hartz AM, Fricker G, Miller DS. Pregnane X receptor up-regulation of P-glycoprotein expression and transport function at the blood-brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;66:413–419. - PubMed
-
- Brenn A, Grube M, Jedlitschky G, Fischer A, Strohmeier B, Eiden M, Keller M, Groschup MH, Vogelgesang S. St. John's Wort reduces beta-amyloid accumulation in a double transgenic Alzheimer's disease mouse model: role of P-glycoprotein. Brain Pathol. 2014;24:18–24. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12069. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Castellano JM, Deane R, Gottesdiener AJ, Verghese PB, Stewart FR, West T, Paoletti AC, Kasper TR, DeMattos RB, Zlokovic BV, Holtzman DM. Low-density lipoprotein receptor overexpression enhances the rate of brain-to-blood Abeta clearance in a mouse model of beta-amyloidosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:15502–15507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206446109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chishti MA, Yang DS, Janus C, Phinney AL, Horne P, Pearson J, Strome R, Zuker N, Loukides J, French J, Turner S, Lozza G, Grilli M, Kunicki S, Morissette C, Paquette J, Gervais F, Bergeron C, Fraser PE, Carlson GA, George-Hyslop PS, Westaway D. Early-onset amyloid deposition and cognitive deficits in transgenic mice expressing a double mutant form of amyloid precursor protein 695. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:21562–21570. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100710200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
