Anti-ApoE antibody given after plaque onset decreases Aβ accumulation and improves brain function in a mouse model of Aβ amyloidosis
- PMID: 24849360
- PMCID: PMC4028501
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0646-14.2014
Anti-ApoE antibody given after plaque onset decreases Aβ accumulation and improves brain function in a mouse model of Aβ amyloidosis
Abstract
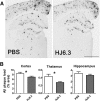
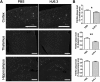
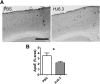
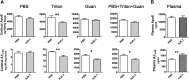
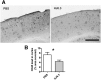
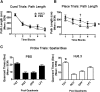
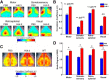
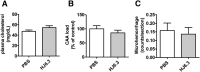
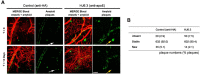
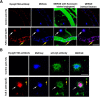
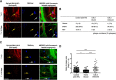
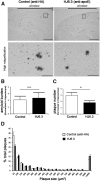
Apolipoprotein E (apoE) is the strongest known genetic risk factor for late onset Alzheimer's disease (AD). It influences amyloid-β (Aβ) clearance and aggregation, which likely contributes in large part to its role in AD pathogenesis. We recently found that HJ6.3, a monoclonal antibody against apoE, significantly reduced Aβ plaque load when given to APPswe/PS1ΔE9 (APP/PS1) mice starting before the onset of plaque deposition. To determine whether the anti-apoE antibody HJ6.3 affects Aβ plaques, neuronal network function, and behavior in APP/PS1 mice after plaque onset, we administered HJ6.3 (10 mg/kg/week) or PBS intraperitoneally to 7-month-old APP/PS1 mice for 21 weeks. HJ6.3 mildly improved spatial learning performance in the water maze, restored resting-state functional connectivity, and modestly reduced brain Aβ plaque load. There was no effect of HJ6.3 on total plasma cholesterol or cerebral amyloid angiopathy. To investigate the underlying mechanisms of anti-apoE immunotherapy, HJ6.3 was applied to the brain cortical surface and amyloid deposition was followed over 2 weeks using in vivo imaging. Acute exposure to HJ6.3 affected the course of amyloid deposition in that it prevented the formation of new amyloid deposits, limited their growth, and was associated with occasional clearance of plaques, a process likely associated with direct binding to amyloid aggregates. Topical application of HJ6.3 for only 14 d also decreased the density of amyloid plaques assessed postmortem. Collectively, these studies suggest that anti-apoE antibodies have therapeutic potential when given before or after the onset of Aβ pathology.
Keywords: Alzheimer's; amyloid; antibody; apolipoprotein E.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/347281-12$15.00/0.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-apoE immunotherapy inhibits amyloid accumulation in a transgenic mouse model of Aβ amyloidosis.J Exp Med. 2012 Nov 19;209(12):2149-56. doi: 10.1084/jem.20121274. Epub 2012 Nov 5. J Exp Med. 2012. PMID: 23129750 Free PMC article.
-
Murine versus human apolipoprotein E4: differential facilitation of and co-localization in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and amyloid plaques in APP transgenic mouse models.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2015 Nov 10;3:70. doi: 10.1186/s40478-015-0250-y. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2015. PMID: 26556230 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid-β protein modulates the perivascular clearance of neuronal apolipoprotein E in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2011 May;118(5):699-712. doi: 10.1007/s00702-010-0572-7. Epub 2011 Jan 6. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2011. PMID: 21210284
-
Understanding the Amyloid Hypothesis in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;68(2):493-510. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180802. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 30883346 Review.
-
Alzheimer's disease: The role of proteins in formation, mechanisms, and new therapeutic approaches.Neurosci Lett. 2023 Nov 20;817:137532. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2023.137532. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Neurosci Lett. 2023. PMID: 37866702 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibiotic-induced perturbations in gut microbial diversity influences neuro-inflammation and amyloidosis in a murine model of Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 21;6:30028. doi: 10.1038/srep30028. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27443609 Free PMC article.
-
CSF beta-amyloid 1-42 - what are we measuring in Alzheimer's disease?Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2015 Feb;2(2):131-9. doi: 10.1002/acn3.160. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25750918 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial signatures and their role in health and disease.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018 Oct;19(10):622-635. doi: 10.1038/s41583-018-0057-5. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30206328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opposing Roles of apolipoprotein E in aging and neurodegeneration.Life Sci Alliance. 2019 Feb 13;2(1):e201900325. doi: 10.26508/lsa.201900325. Print 2019 Feb. Life Sci Alliance. 2019. PMID: 30760557 Free PMC article.
-
APOE ε4 Allele Is Associated with Elevated Levels of CSF VILIP-1 in Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020 Apr 8;16:923-931. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S235395. eCollection 2020. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020. PMID: 32308396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashford JW. ApoE4: is it the absence of good or the presence of bad? J Alzheimers Dis. 2002;4:141–143. - PubMed
-
- Bales KR, Verina T, Cummins DJ, Du Y, Dodel RC, Saura J, Fishman CE, DeLong CA, Piccardo P, Petegnief V, Ghetti B, Paul SM. Apolipoprotein E is essential for amyloid deposition in the APP(V717F) transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:15233–15238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.26.15233. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bard F, Cannon C, Barbour R, Burke RL, Games D, Grajeda H, Guido T, Hu K, Huang J, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K, Kholodenko D, Lee M, Lieberburg I, Motter R, Nguyen M, Soriano F, Vasquez N, Weiss K, Welch B, et al. Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid beta-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat Med. 2000;6:916–919. doi: 10.1038/78682. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
