Optogenetic control of serotonin and dopamine release in Drosophila larvae
- PMID: 24849718
- PMCID: PMC4140588
- DOI: 10.1021/cn500044b
Optogenetic control of serotonin and dopamine release in Drosophila larvae
Abstract
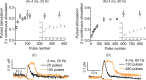
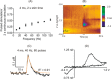
Optogenetic control of neurotransmitter release is an elegant method to investigate neurobiological mechanisms with millisecond precision and cell type-specific resolution. Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) can be expressed in specific neurons, and blue light used to activate those neurons. Previously, in Drosophila, neurotransmitter release and uptake have been studied after continuous optical illumination. In this study, we investigated the effects of pulsed optical stimulation trains on serotonin or dopamine release in larval ventral nerve cords. In larvae with ChR2 expressed in serotonergic neurons, low-frequency stimulations produced a distinct, steady-state response while high-frequency patterns were peak shaped. Evoked serotonin release increased with increasing stimulation frequency and then plateaued. The steady-state response and the frequency dependence disappeared after administering the uptake inhibitor fluoxetine, indicating that uptake plays a significant role in regulating the extracellular serotonin concentration. Pulsed stimulations were also used to evoke dopamine release in flies expressing ChR2 in dopaminergic neurons and similar frequency dependence was observed. Release due to pulsed optical stimulations was modeled to determine the uptake kinetics. For serotonin, Vmax was 0.54 ± 0.07 μM/s and Km was 0.61 ± 0.04 μM; and for dopamine, Vmax was 0.12 ± 0.03 μM/s and Km was 0.45 ± 0.13 μM. The amount of serotonin released per stimulation pulse was 4.4 ± 1.0 nM, and the amount of dopamine was 1.6 ± 0.3 nM. Thus, pulsed optical stimulations can be used to mimic neuronal firing patterns and will allow Drosophila to be used as a model system for studying mechanisms underlying neurotransmission.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Comparison of dopamine kinetics in the larval Drosophila ventral nerve cord and protocerebrum with improved optogenetic stimulation.J Neurochem. 2015 Nov;135(4):695-704. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13286. Epub 2015 Sep 18. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26296526 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative evaluation of serotonin release and clearance in Drosophila.J Neurosci Methods. 2009 May 15;179(2):300-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2009.02.013. Epub 2009 Mar 4. J Neurosci Methods. 2009. PMID: 19428541 Free PMC article.
-
Fast-Scan Cyclic Voltammetry (FSCV) Detection of Endogenous Octopamine in Drosophila melanogaster Ventral Nerve Cord.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016 Aug 17;7(8):1112-9. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00070. Epub 2016 Jul 1. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27326831 Free PMC article.
-
Big Lessons from Tiny Flies: Drosophila melanogaster as a Model to Explore Dysfunction of Dopaminergic and Serotonergic Neurotransmitter Systems.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 16;19(6):1788. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061788. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29914172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multisite intracerebral microdialysis to study the mechanism of L-DOPA induced dopamine and serotonin release in the parkinsonian brain.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 May 15;4(5):680-92. doi: 10.1021/cn400046e. Epub 2013 Apr 15. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23541043 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A pair of dopaminergic neurons DAN-c1 mediate Drosophila larval aversive olfactory learning through D2-like receptors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 6:2024.01.15.575767. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.15.575767. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Elife. 2025 Aug 13;13:RP100890. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100890. PMID: 38293177 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A pair of dopaminergic neurons DAN-c1 mediate Drosophila larval aversive olfactory learning through D2-like receptors.Elife. 2025 Aug 13;13:RP100890. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100890. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40801811 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of dopamine kinetics in the larval Drosophila ventral nerve cord and protocerebrum with improved optogenetic stimulation.J Neurochem. 2015 Nov;135(4):695-704. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13286. Epub 2015 Sep 18. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26296526 Free PMC article.
-
SSRI antidepressants differentially modulate serotonin reuptake and release in Drosophila.J Neurochem. 2022 Sep;162(5):404-416. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15658. Epub 2022 Jul 9. J Neurochem. 2022. PMID: 35736504 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Relationship between Biased and Unbiased Measures of Dopamine Release and Clearance.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022 May 18;13(10):1534-1548. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00033. Epub 2022 Apr 28. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35482592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyden E. S.; Zhang F.; Bamberg E.; Nagel G.; Deisseroth K. (2005) Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1263–1268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

