Heritability and clinical determinants of serum indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate, candidate biomarkers of the human microbiome enterotype
- PMID: 24850265
- PMCID: PMC4029585
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079682
Heritability and clinical determinants of serum indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate, candidate biomarkers of the human microbiome enterotype
Abstract
Background: Indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate are unique microbial co-metabolites. Both co-metabolites have been involved in the pathogenesis of accelerated cardiovascular disease and renal disease progression. Available evidence suggests that indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate may be considered candidate biomarkers of the human enterotype and may help to explain the link between diet and cardiovascular disease burden.
Objective and design: Information on clinical determinants and heritability of indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate serum is non-existing. To clarify this issue, the authors determined serum levels of indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate in 773 individuals, recruited in the frame of the Flemish Study on Environment, Genes and Health Outcomes (FLEMENGHO study).
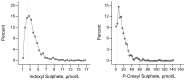
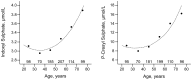
Results: Serum levels of indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate amounted to 3.1 (2.4-4.3) and 13.0 (7.4-21.5) μM, respectively. Regression analysis identified renal function, age and sex as independent determinants of both co-metabolites. Both serum indoxyl sulfate (h2 = 0.17) and p-cresyl sulfate (h2 = 0.18) concentrations showed moderate but significant heritability after adjustment for covariables, with significant genetic and environmental correlations for both co-metabolites.
Limitations: Family studies cannot provide conclusive evidence for a genetic contribution, as confounding by shared environmental effects can never be excluded.
Conclusions: The heritability of indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate is moderate. Besides genetic host factors and environmental factors, also renal function, sex and age influence the serum levels of these co-metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
p-Cresyl sulfate and indoxyl sulfate in hemodialysis patients.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Dec;4(12):1932-8. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02940509. Epub 2009 Oct 15. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19833905 Free PMC article.
-
Renal clearance and intestinal generation of p-cresyl sulfate and indoxyl sulfate in CKD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Sep;8(9):1508-14. doi: 10.2215/CJN.00300113. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23813557 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins during Hemodialysis Using a Binding Competitor.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Mar 7;14(3):394-402. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05240418. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30755453 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-Analysis of the Associations of p-Cresyl Sulfate (PCS) and Indoxyl Sulfate (IS) with Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 14;10(7):e0132589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132589. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26173073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Removal of protein-bound uraemic toxins by haemodialysis.Blood Purif. 2013;35 Suppl 2:20-5. doi: 10.1159/000350843. Epub 2013 May 3. Blood Purif. 2013. PMID: 23676831 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Metabolomics in Pediatric Asthma: Prediction, Diagnosis and Personalized Treatment.Metabolites. 2021 Apr 18;11(4):251. doi: 10.3390/metabo11040251. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33919626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highlighting Levels of Indoxyl Sulphate among Critically Ill Patients with Acute Nephrotoxicity; Correlations Between Indoxyl Sulphate Levels and Patients' Characteristics.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Jul;10(2):266-279. doi: 10.52547/rbmb.10.2.266. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34604416 Free PMC article.
-
Gut-Microbiota-Metabolite Axis in Early Renal Function Decline.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 4;10(8):e0134311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134311. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26241311 Free PMC article.
-
Indoxyl sulfate associates with cardiovascular phenotype in children with chronic kidney disease.Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Dec;34(12):2571-2582. doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04331-6. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31428929
-
Semi-automated NMR Pipeline for Environmental Exposures: New Insights on the Metabolomics of Smokers versus Non-smokers.Pac Symp Biocomput. 2021;26:316-327. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2021. PMID: 33691028 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

