Brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptor availability and response to smoking cessation treatment: a randomized trial
- PMID: 24850280
- PMCID: PMC4634637
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.138
Brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptor availability and response to smoking cessation treatment: a randomized trial
Abstract
Importance: Cigarette smoking leads to upregulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) in the human brain, including the common α4β2* nAChR subtype. While subjective aspects of tobacco dependence have been extensively examined as predictors of quitting smoking with treatment, no studies to our knowledge have yet reported the relationship between the extent of pretreatment upregulation of nAChRs and smoking cessation.
Objective: To determine whether the degree of nAChR upregulation in smokers predicts quitting with a standard course of treatment.
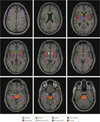
Design, setting, and participants: Eighty-one tobacco-dependent cigarette smokers (volunteer sample) underwent positron emission tomographic (PET) scanning of the brain with the radiotracer 2-FA followed by 10 weeks of double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment with nicotine patch (random assignment). Pretreatment specific binding volume of distribution (VS/fP) on PET images (a value that is proportional to α4β2* nAChR availability) was determined for 8 brain regions of interest, and participant-reported ratings of nicotine dependence, craving, and self-efficacy were collected. Relationships between these pretreatment measures, treatment type, and outcome were then determined. The study took place at academic PET and clinical research centers.
Main outcomes and measures: Posttreatment quit status after treatment, defined as a participant report of 7 or more days of continuous abstinence and an exhaled carbon monoxide level of 3 ppm or less.
Results: Smokers with lower pretreatment VS/fP values (a potential marker of less severe nAChR upregulation) across all brain regions studied were more likely to quit smoking (multivariate analysis of covariance, F8,69 = 4.5; P < .001), regardless of treatment group assignment. Furthermore, pretreatment average VS/fP values provided additional predictive power for likelihood of quitting beyond the self-report measures (stepwise binary logistic regression, likelihood ratio χ21 = 19.8; P < .001).
Conclusions and relevance: Smokers with less upregulation of available α4β2* nAChRs have a greater likelihood of quitting with treatment than smokers with more upregulation. In addition, the biological marker studied here provided additional predictive power beyond subjectively rated measures known to be associated with smoking cessation outcome. While the costly, time-consuming PET procedure used here is not likely to be used clinically, simpler methods for examining α4β2* nAChR upregulation could be tested and applied in the future to help determine which smokers need more intensive and/or lengthier treatment.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT01526005.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment for tobacco dependence: effect on brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptor density.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Jul;38(8):1548-56. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.53. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23429692 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Decreased Nicotinic Receptor Availability in Smokers with Slow Rates of Nicotine Metabolism.J Nucl Med. 2015 Nov;56(11):1724-9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.155002. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Nucl Med. 2015. PMID: 26272810 Free PMC article.
-
Brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptor occupancy: effect of smoking a denicotinized cigarette.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009 Apr;12(3):305-16. doi: 10.1017/S146114570800922X. Epub 2008 Aug 18. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18706128 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The contribution of agonist and antagonist activities of α4β2* nAChR ligands to smoking cessation efficacy: a quantitative analysis of literature data.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Sep;235(9):2479-2505. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4921-9. Epub 2018 Jul 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29980822 Review.
-
Varenicline: a first-line treatment option for smoking cessation.Clin Ther. 2009 Mar;31(3):463-91. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.03.021. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19393839 Review.
Cited by
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor availability in cigarette smokers: effect of heavy caffeine or marijuana use.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016 Sep;233(17):3249-57. doi: 10.1007/s00213-016-4367-x. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27370018 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of smoking cessation with treatment: the emerging contribution of brain imaging research.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 May;40(6):1309-10. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.31. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25868069 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cholinergic system adaptations are associated with cognitive function in people recently abstinent from smoking: a (-)-[18F]flubatine PET study.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023 Mar;48(4):683-689. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01535-1. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36681758 Free PMC article.
-
Thalamic volume and functional connectivity are associated with nicotine dependence severity and craving.Addict Biol. 2023 Jan;28(1):e13261. doi: 10.1111/adb.13261. Addict Biol. 2023. PMID: 36577730 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights in the Involvement of the Endocannabinoid System and Natural Cannabinoids in Nicotine Dependence.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 10;22(24):13316. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413316. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948106 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mokdad AH, Marks JS, Stroup DF, Gerberding JL. Actual causes of death in the United States, 2000. JAMA. 2004;291(10):1238–1245. - PubMed
-
- Bartal M. Health effects of tobacco use and exposure. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2001;56(6):545–554. - PubMed
-
- Leistikow BN, Martin DC, Milano CE. Fire injuries, disasters, and costs from cigarettes and cigarette lights: a global overview. Prev Med. 2000;31(2, pt1):91–99. - PubMed
-
- Leistikow BN. The human and financial costs of smoking. Clin Chest Med. 2000;21(1):189–197. x–xi. - PubMed
-
- Leistikow BN, Miller TR. The health care costs of smoking. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(7):471. author reply 472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

