Structure-function of CD36 and importance of fatty acid signal transduction in fat metabolism
- PMID: 24850384
- PMCID: PMC4329921
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071812-161220
Structure-function of CD36 and importance of fatty acid signal transduction in fat metabolism
Abstract
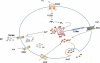
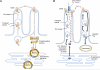
CD36 (cluster of differentiation 36) is a scavenger receptor that functions in high-affinity tissue uptake of long-chain fatty acids (FAs) and contributes under excessive fat supply to lipid accumulation and metabolic dysfunction. This review describes recent evidence regarding the CD36 FA binding site and a potential mechanism for FA transfer. It also presents the view that CD36 and FA signaling coordinate fat utilization, a view that is based on newly identified CD36 actions that involve oral fat perception, intestinal fat absorption, secretion of the peptides cholecystokinin and secretin, regulation of hepatic lipoprotein output, activation of beta oxidation by muscle, and regulation of the production of the FA-derived bioactive eicosanoids. Thus abnormalities of fat metabolism and the associated pathology might involve dysfunction of CD36-mediated signal transduction in addition to the changes in FA uptake.
Keywords: CCK; FA binding; VLDL; calcium; chylomicron; eicosanoid; fat taste; phospholipase; secretin.
Figures


References
-
- Abumrad NA, el-Maghrabi MR, Amri EZ, Lopez E, Grimaldi PA. Cloning of a rat adipocyte membrane protein implicated in binding or transport of long-chain fatty acids that is induced during preadipocyte differentiation. Homology with human CD36. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:17665–8. - PubMed
-
- Babnigg G, Bowersox SR, Villereal ML. The role of pp60c-src in the regulation of calcium entry via store-operated calcium channels. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29434–7. - PubMed
-
- Baillie AGS, Coburn CT, Abumrad NA. Reversible binding of long-chain fatty acids to purified FAT, the adipose CD36 homolog. J Membr Biol. 1996;153:75–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

