Selective inhibitors of a PAF biosynthetic enzyme lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 2
- PMID: 24850807
- PMCID: PMC4076079
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M049205
Selective inhibitors of a PAF biosynthetic enzyme lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 2
Abstract
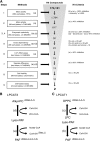
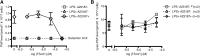
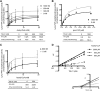
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is a potent pro-inflammatory phospholipid mediator. In response to extracellular stimuli, PAF is rapidly biosynthesized by lyso-PAF acetyltransferase (lyso-PAFAT). Previously, we identified two types of lyso-PAFATs: lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase (LPCAT)1, mostly expressed in the lungs where it produces PAF and dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine essential for respiration, and LPCAT2, which biosynthesizes PAF and phosphatidylcholine (PC) in the inflammatory cells. Under inflammatory conditions, LPCAT2, but not LPCAT1, is activated and upregulated to produce PAF. Thus, it is important to develop inhibitors specific for LPCAT2 in order to ameliorate PAF-related inflammatory diseases. Here, we report the first identification of LPCAT2-specific inhibitors, N-phenylmaleimide derivatives, selected from a 174,000-compound library using fluorescence-based high-throughput screening followed by the evaluation of the effects on LPCAT1 and LPCAT2 activities, cell viability, and cellular PAF production. Selected compounds competed with acetyl-CoA for the inhibition of LPCAT2 lyso-PAFAT activity and suppressed PAF biosynthesis in mouse peritoneal macrophages stimulated with a calcium ionophore. These compounds had low inhibitory effects on LPCAT1 activity, indicating that adverse effects on respiratory functions may be avoided. The identified compounds and their derivatives will contribute to the development of novel drugs for PAF-related diseases and facilitate the analysis of LPCAT2 functions in phospholipid metabolism in vivo.
Keywords: LPCAT2 inhibitor; N-phenylmaleimide derivatives; TSI-01; fluorescent probe; high-throughput screening; inflammation; lipid mediator; lyso-PAF acetyltransferase; lysophospholipid acyltransferase; platelet-activating factor.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel noninflammatory biosynthetic pathway of platelet-activating factor.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 25;283(17):11097-106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708909200. Epub 2008 Feb 19. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18285344
-
Rapid production of platelet-activating factor is induced by protein kinase Cα-mediated phosphorylation of lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 2 protein.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 30;289(22):15566-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.558874. Epub 2014 Apr 17. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24742674 Free PMC article.
-
Mutagenesis and homology modeling reveal a predicted pocket of lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 2 to catch Acyl-CoA.FASEB J. 2021 Jun;35(6):e21501. doi: 10.1096/fj.202002591R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33956375 Free PMC article.
-
[Lysophospholipid acyltransferase and platelet-activating factor (PAF) biosynthetic enzyme].Seikagaku. 2008 Feb;80(2):110-3. Seikagaku. 2008. PMID: 18341030 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Transmembrane signalling and paf-acether biosynthesis.Lipids. 1991 Dec;26(12):1034-7. doi: 10.1007/BF02536497. Lipids. 1991. PMID: 1819687 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Platelet-Activating Factor Synthesis Facilitates Acute and Delayed Effects of Ethanol-Intoxicated Thermal Burn Injury.J Invest Dermatol. 2018 Nov;138(11):2461-2469. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.04.039. Epub 2018 May 30. J Invest Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29857067 Free PMC article.
-
Forty Years Since the Structural Elucidation of Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF): Historical, Current, and Future Research Perspectives.Molecules. 2019 Dec 3;24(23):4414. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234414. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31816871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relief from neuropathic pain by blocking of the platelet-activating factor-pain loop.FASEB J. 2017 Jul;31(7):2973-2980. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601183R. Epub 2017 Mar 24. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28341636 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipases A2 as biomarkers in acute respiratory distress syndrome.Biomed J. 2021 Dec;44(6):663-670. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2021.08.005. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 34478892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of LPCATs Highlights the Prognostic and Immunological Values of LPCAT1/4 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Nov 30;14:9117-9130. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S344723. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34876845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., Stafforini D. M., McIntyre T. M. 2000. Platelet-activating factor and related lipid mediators. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69: 419–445 - PubMed
-
- Ishii S., Shimizu T. 2000. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor and genetically engineered PAF receptor mutant mice. Prog. Lipid Res. 39: 41–82 - PubMed
-
- Kihara Y., Yanagida K., Masago K., Kita Y., Hishikawa D., Shindou H., Ishii S., Shimizu T. 2008. Platelet-activating factor production in the spinal cord of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis mice via the group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A2-lyso-PAFAT axis. J. Immunol. 181: 5008–5014 - PubMed
-
- Shimizu T. 2009. Lipid mediators in health and disease: enzymes and receptors as therapeutic targets for the regulation of immunity and inflammation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 49: 123–150 - PubMed
-
- Shindou H., Ishii S., Yamamoto M., Takeda K., Akira S., Shimizu T. 2005. Priming effect of lipopolysaccharide on acetyl-coenzyme A:lyso-platelet-activating factor acetyltransferase is MyD88 and TRIF independent. J. Immunol. 175: 1177–1183 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

